Waspadai dan Cegah Pneumonia dan Diare di Masa Pandemi Covid-19
Awareness and Prevention Pneumonia and Diarrhea in Pandemic Covid-19
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33084/pengabdianmu.v7i3.2752Keywords:
Pneumonia, Diarrhea, Covid-19 pandemicAbstract
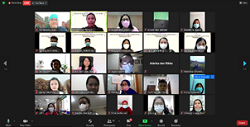
The leading causes of death in children vary according to age. Children under five years are vulnerable to infectious diseases such as malaria, pneumonia, diarrhea, HIV, and tuberculosis. Pneumonia is a contagious infectious disease and the most significant cause of death in children under five. Diarrhea is the second leading cause of death in children under five. Diarrhea is the leading cause of malnutrition in children under five. Indonesia is included in the top ten countries with the highest number of deaths in children under five years in 2019. This activity aims to increase knowledge of the community, especially mothers, about pneumonia and diarrhea. The method used was a virtual seminar. The webinar was held on May 7, 2021, using a zoom meeting with 87 participants. The majority of participants had never had pneumonia (98.8%). And the number of participants who had experienced diarrhea was 64 participants (80%). The results showed an increase in knowledge after attending the virtual seminar. The average (mean) knowledge score increased by 1.97. The majority of participants gave excellent marks on activities related to the topic/theme of the event, speakers, audiovisual quality, and question and answer sessions.
Downloads
References
American College of Gastroenterology. 2020. Diarrhea in Children. https://gi.org/topics/diarrhea-in-children/
Bello, S., Menéndez, R., Torres, A., Reyes, S., Zalacain, R., Capelastegui, A., et al. 2014. Tobacco smoking increases the risk for death from pneumococcal pneumonia. Chest. 146(4):1029-1037. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.13-2853
Chen, J., Wan, C.M., Gong, S.T., Fang, F., Sun, M., Qian, Y., et al. 2018. Chinese clinical practice guidelines for acute infectious diarrhea in children. World Journal of Pediatrics. 14(5):429-436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12519-018-0190-2
Christy, M.Y. 2014. Factors Associated with Diarrheal Dehydration in Toddlers at Kalijudan Health Center Work Area. Jurnal Berkala Epidemiologi. 2(3):297–308. https://doi.org/10.20473/jbe.V2I32014.297-308
Guarino, A., Dupont, C., Gorelov, A.V., Gottrand, F., Lee, J.K., Lin, Z., et al. 2012. The management of acute diarrhea in children in developed and developing areas: From evidence base to clinical practice. Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 13(1):17-26. https://doi.org/10.1517/14656566.2011.634800
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. 2019. Pneumonia, Penyebab Kematian Utama Balita. https://www.kemkes.go.id/article/view/410/pneumonia-penyebab-kematian-utama-balita.html#:~:text=Pneumonia%20merupakan%20pembunuh%20utama%20anak,banyak%20perhatian%20terhadap%20penyakit%20ini.
Meliyanti, A., Rusmawatiningtyas, D., Makrufardi, F., Arguni, E. 2021. Factors associated with mortality in pediatric pneumonia patients supported with mechanical ventilation in developing country. Heliyon. 7(5):e07063. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07063
Mokomane, M., Kasvosve, I., de Melo, E., Pernica, J.M., Goldfarb, D.M. 2018. The global problem of childhood diarrhoeal diseases: emerging strategies in prevention and management. Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease. 5(1):29-43. https://doi.org/10.1177/2049936117744429
Ngari, M.M., Obiero, C., Mwangome, M.K., Nyaguara, A., Mturi, N., Murunga, S., et al. 2021. Mortality during and following hospital admission among school-aged children: a cohort study. Wellcome Open Research. 5:234. https://doi.org/10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16323.2
Simoes, E.A.F., Cherian, T., Chow, J., Shahid-Salles, S.A., Laxminarayan, R., John, J. Acute Respiratory Infections in Children. In: Jamison, D.T., Breman, J.G., Measham, A.R., Alleyne, G., Claeson, M., Evans, D.B., et al., editors. Disease Control Priorities in Developing Countries. 2nd edition. Washington (DC): The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development / The World Bank; 2006. Chapter 25.
Takanashi, K., Chonan, Y., Quyen, D.T., Khan, N.C., Poudel, K.C., Jimba, M. 2009. Survey of food-hygiene practices at home and childhood diarrhoea in Hanoi, Viet Nam. Journal of Health, Population, and Nutrition. 27(5):602-611. https://doi.org/10.3329/jhpn.v27i5.3636
Tsai, J., Homa, D.M., Gentzke, A.S., Mahoney, M., Sharapova, S.R., Sosnoff, C.S., et al. 2018. Exposure to Secondhand Smoke Among Nonsmokers - United States, 1988-2014. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 67(48):1342-1346. https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.mm6748a3
Ugboko, H.U., Nwinyi, O.C., Oranusi, S.U., Oyewale, J.O. 2020. Childhood diarrhoeal diseases in developing countries. Heliyon. 6(4):e03690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03690
World Health Organization. 2021. Child mortality and causes of death. https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/topic-details/GHO/child-mortality-and-causes-of-death#:~:text=Globally%2C%20infectious%20diseases%2C%20including%20pneumonia,death%20for%20children%20under%20five.
World Health Organization. 2020. Children: improving survival and well-being. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/children-reducing-mortality
World Health Organization. 2017. Diarrhoeal disease. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diarrhoeal-disease
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- Author grant the journal, right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into a separate, additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of published articles of work (eg, post-institutional repository) or publish it in a book, with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License










