Edukasi Kesehatan tentang Penyakit Degeneratif dan Informasi Obat di Kampung Biru, Banjarmasin, Indonesia Health Education on Degenerative Diseases and Medication Information in Kampung Biru, Banjarmasin, Indonesia
Main Article Content
Abstract
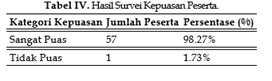
Degenerative diseases such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia are major global health concerns with high prevalence in Indonesia, including in Kampung Biru, Banjarmasin. This community service initiative aimed to enhance public knowledge about the prevention and management of degenerative diseases, while also providing medication information through the Drug Information Service (DIS). The program involved 58 participants who underwent health screenings (blood pressure, blood glucose, cholesterol, and uric acid levels), disease-specific group education, and DIS sessions conducted by pharmacists. Results showed a 60.34% improvement in participants' knowledge, with a 98.27% satisfaction rate. Data analysis revealed a higher prevalence of these diseases among the elderly (aged 45 years and above), aligning with national epidemiological trends. The program demonstrated the effectiveness of a collaborative approach involving academics, healthcare professionals, and the community in promoting health literacy and preventive care.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- Author grant the journal, right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into a separate, additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of published articles of work (eg, post-institutional repository) or publish it in a book, with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
References
Ayu, M. D., & Syaripuddin, A. (2019). Peran apoteker dalam edukasi hipertensi berbasis komunitas. Jurnal Farmasi Klinis Indonesia, 8(2), 103–108. https://doi.org/10.2147/PPA.S394855
Budiyati, L. (2023). Health Promotion Model dan implementasinya dalam praktik farmasi komunitas. Jurnal Promkes, 11(1), 1–7. https://jptam.org/index.php/jptam/issue/current
Coughlin, S. S., Smith, S. A., & Fernandez, M. E. (2020). Health literacy and patient education. Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education, 10(3), 1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0711.1000702
Fibra, M., et al. (2021). Kejadian Diabetes Melitus Tipe II pada Lansia. Jurnal Kedokteran dan Kesehatan UMJ JKK, 17(1), 128–136. https://doi.org/10.24853/jkk.17.1.9-20
Hasana, N. (2021). Edukasi Gizi pada Penderita Asam Urat. Nusantara Hasana Journal, 1(6), 91–94. https://doi.org/10.55927/fjst.v2i9.5723
Hintari, S., & Fibriana, A. I. (2023). Hipertensi pada Penduduk Usia Produktif. HIGEIA (Journal of Public Health Research and Development), 7(2), 209–218. https://doi.org/10.15294/higeia.v7i1.63472
IDF. (2019). IDF Diabetes Atlas (9th ed.). International Diabetes Federation.
Kementerian Kesehatan RI. (2018). Laporan Nasional Riskesdas 2018. Jakarta: Kemenkes RI. https://repository.kemkes.go.id/book/1323
Kemenkes RI. (2023). Survei Kesehatan Indonesia (SKI) Tahun 2023. Jakarta: Kemenkes RI.
Kilic, M., Uzun, S., & Saip, E. (2016). The effect of education on the level of knowledge and compliance of hypertension patients. International Journal of Caring Sciences, 9(1), 19–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcac.2016.01.003
Notoatmodjo, S. (2012). Promosi kesehatan dan perilaku kesehatan. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta. https://repositori.uin-alauddin.ac.id/19791/1/2021_Book%20Chapter_Promosi%20Kesehatan%20dan%20Perilaku%20Kesehatan.pdf
Sari, D., et al. (2024). Faktor Risiko Hiperkolesterolemia pada Usia Dewasa. Journal of TSCS1Kep, 9(2), 23–30. https://ejournal.annurpurwodadi.ac.id/index.php/TSCS1Kep/article/download/570/590
Sulistyorini, R., & Amukti, I. (2024). Dampak keterlibatan apoteker terhadap peningkatan kesadaran kesehatan masyarakat. Jurnal Pengabdian Farmasi Indonesia, 3(2), 45–52. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382735713_Upaya_promosi_kesehatan_dan_pencegahan_hipertensi_pada_masyarakat
Wahyudi, E., Ramadhani, R., & Rahayu, T. (2024). Pengaruh penyuluhan terhadap pengetahuan lansia tentang hipertensi. Jurnal Ahmar Educatia, 4(1), 55–62. https://doi.org/10.53770/amjpm.v4i1.345
WHO. (2021). Global status report on noncommunicable diseases. Geneva: World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases
Yuniarti, R., & Syafriati, R. (2022). Pendekatan teori Nola Pender dalam promosi kesehatan komunitas. Jurnal Ilmiah Keperawatan, 14(1), 10–16. https://journal.umpr.ac.id/index.php/pengabdianmu/article/download/10232/5952/42166