Peningkatan Pengetahuan tentang Gizi di Masa Pandemi untuk Pencegahan Covid-19 Improvement of Nutrition Knowledge during Pandemic for Covid-19 Disease Prevention
Main Article Content
Abstract
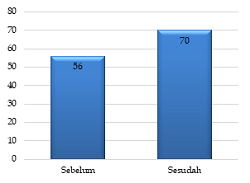
Nutritional fulfillment is one of the essential factors to prevent the Covid-19 disease. The term balanced nutrition consists of several points: balanced consumption of staple food, the source of protein, fruit, and vegetables, and also drinking an adequate amount of water. Several specific nutrients are also involved in strengthening the immune system, such as vitamin A, C, E, B6, folic acid, zinc, selenium, and iron. The balanced diet practices are affected by nutrition knowledge and further underlined the importance of an educational approach to knowledge improvement of its principles to prevent Covid-19 disease. The intervention conducted through an online meeting platform with a pre-post test was applied to measure the level of knowledge. There were 92 participants in this international event, with the knowledge score improvement was 25% higher than the pre-test mean score. The highest rose was in the vegetables daily intake recommendation and the highest vitamin C source. In conclusion, sustainable educational intervention is important to improve the community’s knowledge about a balanced diet that plays a role in Covid-19 disease prevention.
Downloads
Article Details
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- Author grant the journal, right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into a separate, additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of published articles of work (eg, post-institutional repository) or publish it in a book, with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
References
Carr, A.C., Rowe, S. 2020. Editorial: The Emerging Role of Vitamin C in The Prevention and Treatment of Covid-19. Nutrients. 12(11):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12113286
Chin, Y.S., Chew, B.H., Widyahening, I.S. 2021. Dietary Practices and Nutrition for the Prevention of Covid-19. RECRUS: Research Newsletter. 1(3):1–5
Egg, S., Wakolbinger, M., Reisser, A., Schätzer, M., Wild, B., Rust, P. 2020. Relationship between nutrition knowledge, education and other determinants of food intake and lifestyle habits among adolescents from urban and rural secondary schools in Tyrol, Western Austria. Public Health Nutrition. 23(17):3136–3147. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1368980020000488
Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. 2020. Panduan Gizi Seimbang Pada Masa Pandemi COVID-19. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia
Mahmud, M.K., Hermana, Nazarina, Marudut, Zulfianto, N.A., Muhayatun, et al. 2018. Tabel Komposisi Pangan Indonesia 2017. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia.
Shalaby, S.I., Awad, M.M., El Dean, H.N., Mohamed, R.A., Gupta, N., Singh, R. 2016. Impact of nutritional health educational program `on elderly persons’ nutritional knowledge, attitude and practice. Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences. 7(3):460-476
Shapu, R.C., Ismail, S., Ahmad, N., Lim, P.Y., Njodi, I.A. 2020. Systematic review: Effect of health education intervention on improving knowledge, attitudes and practices of adolescents on malnutrition. Nutrients. 12(8):2426. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082426
Spronk, I., Kullen, C., Burdon, C., O’Connor, H. 2014. Relationship between nutrition knowledge and dietary intake. British Journal of Nutrition. 111(10):1713–1726. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114514000087
Sulistyawati, S., Rokhmayanti, R., Aji, B., Wijayanti, S.P.M., Hastuti, S.K.W., Sukesi, T.W., et al. 2021. Knowledge, attitudes, practices and information needs during the covid-19 pandemic in indonesia. Risk Management and Healthcare Policy. 14:163–175. https://doi.org/10.2147/RMHP.S288579
World Health Organization. 2020. Eat fresh and unprocessed foods every day Drink enough water every day. http://www.emro.who.int/nutrition/nutrition-infocus/nutrition-advice-for-adults-during-the-covid-19-outbreak.html