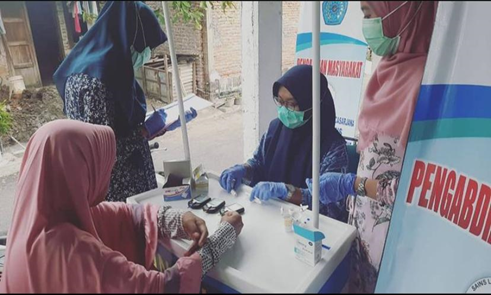
Penyuluhan dan Pemeriksaan Kesehatan sebagai Strategi Menghadapi Masa Transisi Menuju Endemi Covid-19 Education and Health examination as a Strategy for Facing the Transition Period Towards the Covid-19 Endemic
Main Article Content
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic is caused by the coronavirus (Sars-CoV-2). Government programs and policies are gradually establishing controlled environments. In the current situation, the government is preparing several strategies to transition the COVID-19 pandemic to endemic status. Endemic conditions certainly do not mean harmless. It is necessary to educate the community so that the current status of COVID-19 does not carry away the community. To provide health education and routine blood tests (glucose, cholesterol, uric acid) for residents in the Amposari RT 05 RW 03 Kelurahan Kedungmundu, Tembalang District, Semarang, as one of the strategies for preventing and controlling COVID-19 during the transition to endemic. Community service was conducted in Amposari RT 05 RW 03, Kedungmundu Village, Tembalang District, Semarang, in three stages: preparation, implementation, and evaluation. Results: The knowledge of 35 respondents improved, with a mean pre-test score of 41.0, increasing to 78.3 after the post-test. The health examination showed that most residents had normal blood glucose and uric acid levels, but the results for cholesterol were dominated by above normal. Conclusion: Following education, there was a significant increase in knowledge, and most residents had higher cholesterol levels than normal. There was a significant increase in knowledge after education was carried out, and most residents had cholesterol levels above normal.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- Author grant the journal, right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into a separate, additional contractual arrangements for non-exclusive distribution of published articles of work (eg, post-institutional repository) or publish it in a book, with acknowledgment of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process, as can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work.
- The article and any associated published material is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
References
Chakraborty, S. Milka, D., Trivikram, R. M., Frederick, A. H., Haden, L. S., John K., et al. (2022). How cholesterol stiffens unsaturated lipid membranes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 117(36), 21896–21905. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2004807117
Handayani, F., Monepa J.M., Patodo, M.S., Sulistiana, R., & Liwang, M.N. (2022). Penyuluhan Manajemen Stress Era Transisi Pandemi Menjadi Endemi Covid-19. Jurnal Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat Nusantara, 3(2), 744-747.
Huang, C., Wang, Y., Li, X., Ren, L., Zhao, J., Hu, Y., Cao, B., et al. (2020). Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet, 395(10223), 497-506. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30183-5
Joyosemito, I. S. & Nasir, N. M. (2021). Gelombang Kedua Pandemi menuju Endemi Covid-19: Analisis Kebijakan Vaksinasi dan Pembatasan Kegiatan Masyarakat di Indonesia. Jurnal Sains Teknologi dalam Pemberdayaan Masyarakat, 2(1), 55-66.
Katzourakis, A. (2022). COVID-19: endemic doesn’t mean harmless. Nature, 601(7894):485. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-00155-x
Lau, H., Khosrawipour, V., Kocbach, P., Mikolajczyk, A., Ichii, H., Schubert, J., et al. (2020). Internationally lost COVID-19 cases. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection, 53(3), 454-458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.013
Mukaromah, A. H., Putri, S. A. P., Nurul, Q, Wijanarko, W., Pratiwi R. H., & Sya’diah, S. (2020). Pemeriksaan Glukosa, Kolesterol dan Asam Urat pada Masyarakat Peserta Car Free Day di Balai Pelatihan Kesehatan (Bapelkes) Kota Semarang. Jurnal Surya Masyarakat, 2(2), 133-138. https://doi.org/10.26714/jsm.2.2.2020.133-138
Nasir, N. M., Joyosemito, I. S., Boerman, B., & Ismaniah. (2021). Kebijakan Vaksinasi COVID-19: Pendekatan Pemodelan Matematika Dinamis Pada Efektivitas Dan Dampak Vaksin Di Indonesia. Jurnal Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat UBJ, 4(2), 191–204. https://doi.org/10.31599/jabdimas.v4i2.662
Putri, G.S.A., Darwamati, S. & Khammaruddin, M. (2022). Edukasi Pencegahan Diabetes Melitus dan Hipertensi Sejak Dini di PantiAsuhan Khaira Ummah Demak Sebagai Sebuah Kewaspadaan di Masa Pandemi. Jurnal Inovasi dan Pengabdian Masyarakat Indonesia, 1(3), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.26714/jipmi.v1i3.21
Rothan, H. A. & Byrareddy, S. N. (2020). The epidemiology and pathogenesis of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. Journal of Autoimmunity, 109, 102433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102433
Saryanti, D. & Nugraheni, D. (2019). Peningkatan pengetahuan masyarakat tentang penyakit diabetes melitus. JPPM (Jurnal Pengabdian dan Pemberdayaan Masyarakat), 3(1), 111-116. https://doi.org/10.30595/jppm.v3i1.3626
Sinto, R. (2022). COVID-19 Pandemic-to-Endemic Transition in Indonesia: What Does the Future Hold? Acta Medica Indonesia, 54(2), 159-160 https://www.actamedindones.org/index.php/ijim/article/view/2158/575
Sulastri, T. & Jufri, M. (2021). Resiliensi di Masa Pandemi: Peran Efikasi Diri dan Persepsi Ancaman COVID-19. Jurnal Penelitian Psikologi, 2(1):25-32. https://doi.org/10.29080/jpp.v12i1.531
Sumangkut, S., Supit, W., & Onibala, F. (2013). Hubungan Pola Makan Dengan Kejadian Penyakit Diabetes Melitus Tipe-2 Di Poli Interna BLU.RSUP. Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Manado. Jurnal Keperawatan, 1(1), 37–39. https://doi.org/10.35790/jkp.v1i1.2235
Syakurah, R. A. & Moudy, J. (2020). Pengetahuan terkait usaha pencegahan Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) di Indonesia. HIGEIA (Journal of Public Health Research and Development), 4(3), 333–346. https://doi.org/10.15294/higeia.v4i3.37844