Illness Risk Perceptions and Efficacy Beliefs Among Indonesian in the Course of COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
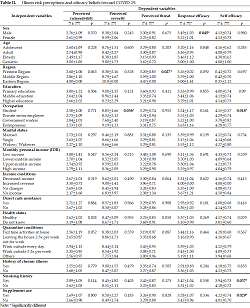
COVID-19, a worldwide pandemic, has posed a significant challenge to public health systems worldwide. Health risk perception and efficacy belief are primary constructs influencing individuals' protective behavior due to the outbreak. Our study investigated each item of illness risk perception, efficacy belief, and its related factors concerning the COVID-19 pandemic. An analytical cross-sectional study was conducted among 227 respondents aged 17 to 70. Data collection was conducted using convenience sampling by distributing the web questionnaire between April and July 2020. Mann-Whitney or Kruskal-Wallis bivariate analysis was performed using SPSS version 21.0 to assess the relationship between individual characteristic factors, illness risk perception, and efficacy belief. The study established that respondents had a medium to a high level of illness risk perception and a reasonable efficacy belief in dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic. Region (p=0.027) and occupation (p=0.036) differences were significantly associated with the threat and severity perception, respectively. Smoking history (p=0.037), supplement use (p=0.029), and occupation (p=0.018) differences were significantly associated with self-efficacy. Meanwhile, gender (p=0.045) differences were significantly associated with response efficacy. Therefore, the public's illness risk perception and efficacy belief could be substantial in planning, modifying, and implementing a coordinated response for risk communication in current and future epidemics.
Full text article
References
2. Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic. Acta Biomed. 2020;91(1):157-60. doi:10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397
3. Djalante R, Lassa J, Setiamarga D, Sudjatma A, Indrawan M, Haryanto B, et al. Review and analysis of current responses to COVID-19 in Indonesia: Period of January to March 2020. Prog Disaster Sci. 2020;6:100091. doi:10.1016/j.pdisas.2020.100091
4. World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-18. Jakarta, Indonesia: WHO Indonesia; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/searo/indonesia/covid19/who-situation-report-18.pdf
5. Alam MM, Fawzi AM, Islam MM, Said J. Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on national security issues: Indonesia as a case study. Secur J. 2022;35(4):1067-86. doi:10.1057/s41284-021-00314-1
6. Lusida MAP, Salamah S, Jonatan M, Wiyogo IO, Asyari CH, Ali ND, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for depression, anxiety, and stress in non-hospitalized asymptomatic and mild COVID-19 patients in East Java province, Indonesia. PLoS One. 2022;17(7):e0270966. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0270966
7. Akbar Z, Aisyawati MS. Coping Strategy, Social Support, and Psychological Distress Among University Students in Jakarta, Indonesia During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Front Psychol. 2021;12:694122. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.694122
8. Abdullah I. COVID-19: Threat and fear in Indonesia. Psychol Trauma Theory Res Pract Policy. 2021;12(5):488-90. doi:10.1037/tra0000878
9. Xiong J, Lipsitz O, Nasri F, Lui LMW, Gill H, Phan L, et al. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on mental health in the general population: A systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2020;277:55–64. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.001
10. Giallonardo V, Sampogna G, Del Vecchio V, Luciano M, Albert U, Carmassi C, et al. The Impact of Quarantine and Physical Distancing Following COVID-19 on Mental Health: Study Protocol of a Multicentric Italian Population Trial. Front psychiatry. 2020;11:533. doi:10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00533
11. Zewdie A, Mose A, Sahle T, Bedewi J, Gashu M, Kebede N, et al. The health belief model's ability to predict COVID-19 preventive behavior: A systematic review. SAGE Open Med. 2022;10:20503121221113668. doi:10.1177/20503121221113668
12. Karl JA, Fischer R, Druică E, Musso F, Stan A. Testing the Effectiveness of the Health Belief Model in Predicting Preventive Behavior During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Case of Romania and Italy. Front Psychol. 2022;12:627575. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.627575
13. Sobkow A, Zaleskiewicz T, Petrova D, Garcia-Retamero R, Traczyk J. Worry, Risk Perception, and Controllability Predict Intentions Toward COVID-19 Preventive Behaviors. Front Psychol. 2020;11:582720. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.582720
14. Ferrer R, Klein WM. Risk perceptions and health behavior. Curr Opin Psychol. 2015;5:85-9. doi:10.1016/j.copsyc.2015.03.012
15. Schneiderman N, Ironson G, Siegel SD. Stress and health: psychological, behavioral, and biological determinants. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2005;1:607-28. doi:10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.1.102803.144141
16. Cipolletta S, Andreghetti GR, Mioni G. Risk Perception towards COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Qualitative Synthesis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19(8):4649. doi:10.3390/ijerph19084649
17. Diotaiuti P, Valente G, Mancone S, Falese L, Bellizzi F, Anastasi D, et al. Perception of Risk, Self-Efficacy and Social Trust during the Diffusion of Covid-19 in Italy. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(7):3427. doi:10.3390/ijerph18073427
18. Nanda RO, Lolita L, Indayati W, Rusdiyanti I, Ikhsanudin A, Mareti S. Knowledge, precautionary actions, and perceived risk of COVID-19 among indonesian people. Int J Public Health Sci. 2021;10(1):8–15. doi:10.11591/ijphs.v10i1.20589
19. Nanda RO, Lolita L, Indayati W, Rusdiyanti I, Nurjannah, Ikhsanudin A, et al. Covid-19 risk perception among Indonesians in early stage of the outbreak. Int J Public Health Sci. 2021;10(2):249–57. doi:10.11591/ijphs.v10i2.20678
20. Lutfi M, Buntuang PCD, Kornelius Y, Erdiyansyah, Hasanuddin B. The impact of social distancing policy on small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Indonesia. Probl Perspect Manag. 2020;18(3):492-503. doi:10.21511/ppm.18(3).2020.40
21. de Zwart O, Veldhuijzen IK, Elam G, Aro AR, Abraham T, Bishop GD, et al. Perceived threat, risk perception, and efficacy beliefs related to SARS and other (emerging) infectious diseases: Results of an international survey. Int J Behav Med. 2009;16(1):30–40. doi:10.1007/s12529-008-9008-2
22. Umamaheswar J, Tan C. “Dad, Wash Your Hands”: Gender, Care Work, and Attitudes toward Risk during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Socius. 2020;6:1-14. doi:10.1177/2378023120964376
23. Griffith DM, Sharma G, Holliday CS, Enyia OK, Valliere M, Semlow AR, et al. Men and COVID-19: A Biopsychosocial Approach to Understanding Sex Differences in Mortality and Recommendations for Practice and Policy Interventions. Prev Chronic Dis. 2020;17:E63. doi:10.5888/pcd17.200247
24. World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-41. Jakarta, Indonesia: WHO Indonesia; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200301-sitrep-41-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=6768306d_2&download=true
25. van der Plaat DA, Madan I, Coggon D, van Tongeren M, Edge R, Muiry R, et al. Risks of COVID-19 by occupation in NHS workers in England. Occup Environ Med. 2022;79(3):176-83. doi:10.1136/oemed-2021-107628
26. Walsh B, Redmond P, Roantree B, Redmond P. Differences in risk of severe outcomes from COVID-19 across occupations in Ireland. ESRI Survey and Statistical Report Series Number 93. Dublin, Ireland: The Economic and Social Research Institute; 2020. doi:10.26504/sustat93
27. Lan FY, Wei CF, Hsu YT, Christiani DC, Kales SN. Work-related COVID-19 transmission in six Asian countries/areas: A follow-up study. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0233588. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233588
28. Kashyap VK, Dhasmana A, Massey A, Kotnala S, Zafar N, Jaggi M, et al. Smoking and COVID-19: Adding Fuel to the Flame. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(18):6581. doi:10.3390/ijms21186581
29. Ahmed N, Maqsood A, Abduljabbar T, Vohra F. Tobacco Smoking a Potential Risk Factor in Transmission of COVID-19 Infection. Pak J Med Sci. 2020;36(COVID19-S4):S104-7. doi:10.12669/pjms.36.covid19-s4.2739
30. Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong SK, Berne MA, et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 2003;426(6965):450-4. doi:10.1038/nature02145
31. Ni W, Yang X, Yang D, Bao J, Li R, Xiao Y, et al. Role of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in COVID-19. Crit Care. 2020;24(1):422. doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03120-0
32. Polverino F. Cigarette Smoking and COVID-19: A Complex Interaction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020;202(3):471–2. doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1646le
33. Alqahtani JS, Oyelade T, Aldhahir AM, Alghamdi SM, Almehmadi M, Alqahtani AS, et al. Prevalence, Severity and Mortality associated with COPD and Smoking in patients with COVID-19: A Rapid Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0233147. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0233147
34. Kumar P, Kumar M, Bedi O, Gupta M, Kumar S, Jaiswal G, et al. Role of vitamins and minerals as immunity boosters in COVID-19. Inflammopharmacology. 2021;29(4):1001-16. doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00826-7
35. Ahmed MH, Hassan A, Molnár J. The Role of Micronutrients to Support Immunity for COVID-19 Prevention. Rev Bras Farmacogn. 2021;31(4):361-74. doi:10.1007/s43450-021-00179-w
36. Sahebnasagh A, Saghafi F, Avan R, Khoshi A, Khataminia M, Safdari M, et al. The prophylaxis and treatment potential of supplements for COVID-19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;887:173530. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173530
37. Mrityunjaya M, Pavithra V, Neelam R, Janhavi P, Halami PM, Ravindra PV. Immune-Boosting, Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Food Supplements Targeting Pathogenesis of COVID-19. Front Immunol. 2020;11:570122. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.570122
38. Handayani W, Insani TD, Fisher M, Gim THT, Mardhotillah S, Adam UEF. Effects of COVID-19 restriction measures in Indonesia: A comparative spatial and policy analysis of selected urban agglomerations. Int J Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022;76:103015. doi:10.1016/j.ijdrr.2022.103015
39. Mya KS, Aye SM, Hlaing WA, Hlaing SS, Aung T, Lwin SMM, et al. Awareness, perceived risk and protective behaviours of Myanmar adults on COVID-19. Int J Commun Med Public Health. 2020;7(5):1627. doi:10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20201530
40. Kwok KO, Li KK, Chan HHH, Yi YY, Tang A, Wei WI, et al. Community Responses during Early Phase of COVID-19 Epidemic, Hong Kong. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26(7):1575–9. doi:10.3201/eid2607.200500
41. Yıldırım M, Güler A. COVID-19 severity, self-efficacy, knowledge, preventive behaviors, and mental health in Turkey. Death Stud. 2020;46(4):979-86. doi:10.1080/07481187.2020.1793434
42. Sulistyawati, Rokhmayanti, Aji B, Wijayanti SPM, Hastuti SKW, Sukesi TW, et al. Knowledge, Attitudes, Practices and Information Needs During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2021;14:163. doi:10.2147/rmhp.s288579
43. Serafini G, Parmiagini B, Amerio A, Aguglia A, Sher L, Amore M. The psychological impact of COVID-19 on the mental health in the general population. QJM. 2020;113(8):531-7. doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcaa201
44. Husnah, Salawati L, Sakdiah, Nazira N, Firdausa S, Nawawi YS. Perception and preventive behavior during COVID-19 pandemic among residents in Banda Aceh, Indonesia: a cross-sectional study. Med J Indones. 2021;30:290-6. doi:10.13181/mji.oa.215674
45. Cori L, Bianchi F, Cadum E, Anthonj C. Risk Perception and COVID-19. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(9):3114. doi:10.3390/ijerph17093114
46. Ghio D, Lawes-Wickwar S, Tang MY, Epton T, Howlett N, Jenkinson E, et al. What influences people's responses to public health messages for managing risks and preventing infectious diseases? A rapid systematic review of the evidence and recommendations. BMJ Open. 2021;11(11):e048750. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-048750
47. Liu PL. COVID-19 information on social media and preventive behaviors: Managing the pandemic through personal responsibility. Soc Sci Med. 2021;277:113928. doi:10.1016/j.socscimed.2021.113928
48. Ayuningtyas D, Haq HU, Utami RRM, Susilia S. Requestioning the Indonesia Government's Public Policy Response to the COVID-19 Pandemic: Black Box Analysis for the Period of January-July 2020. Front Public Health. 2021;9:612994. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.612994
Authors
Copyright (c) 2022 Lolita Lolita, Azis Ikhsanudin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.