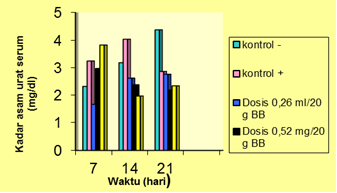
Effect of Giving Celecoxib on Uric Acid Level on Mice
Abstract
Celecoxib is a breakthrough for pain relievers under the trade name Celebrex®, which is a Non-Steroid Anti-Inflammatory drug with its activity as an analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory. The purpose of this study was to find out the effect of celecoxib on blood uric acid levels of female white mice was induced with fresh cow liver extract. Experimental animals were divided into five groups, namely the control group (-), the control group (+) and the three dose groups, respectively 0.26, 0.52 and 1.04 mg/20 g. Observations were made on 7, 14 and 21 days with the Enzymatic Photometric method. The results showed that administration of celecoxib suspension at a dose of 0.26, 0.52 and 1.04 mg/20 g did not affect blood uric acid levels when compared with controls (P> 0.05).
Full text article
References
Raval, M.K., Sathesh Babu, P.R., Thimmasetty, J., Parikh, R.K., Sheth, N.R., Subrahmanyam, C.V.S. 2010. Influence of solvents on the crystal habit and properties of rofecoxib and celecoxib: No evidence of polymorphism. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results. 1(2):40-50.
Zarghi, A., Arfaei, S. 2011. Selective COX-2 Inhibitors: A Review of Their Structure-Activity Relationships. Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Research. 10(4):655-683.
Hediger, M.A. 2004. Physiology and biochemistry of uric acid. Therapeutische Umschau. 61(9):541-545.
Murray, R.K. 2012. Harper's illustrated biochemistry (29th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Medical.
Suyono, S. 2001. Buku Ajar Penyakit Dalam (3rd ed.). Jakarta Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Indonesia.
Milind, P., Sushila, K., Neeraj, S. 2013. Understanding Gout Beyond Doubt. International Research Journal of Pharmacy. 4(9):25-34.
Ong, C.K.S., Lirk, P., Tan, C.H., Seymour, R.A. 2007. An Evidence-Based Update on Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Clinical Medicine & Research. 5(1):19-34.
Zarraga, I.G.E., Schwarz, E.R. 2007. Coxibs and Heart Disease: What We Have Learned and What Else We Need to Know. Journal of The American College of Cardiology. 49(1):1-14.
Lascelles, B.D.X., Court, M.H., Hardie, E.M., Robertson, S.A. 2007. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in cats: a review. Veterinary Anaesthesia and Analgesia. 34:228-250.
Pasalic, D., Marinkovic, N., Feher-Turkovic, L. 2012. Uric acid as one of the important factors in multifactorial disorders – facts and controversies. Biochemia Medica. 22(1):63-75.
Burns, C.M., Wortmann, R.L. 2012. Latest evidence on gout management: what the clinician needs to know. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 3(6):271-286.
Authors
Copyright (c) 2018 Sara Surya

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.