Marine Sponge Xestospongia sp.: A Promising Source for Tuberculosis Drug Development - Computational Insights into Mycobactin Biosynthesis Inhibition
Abstract
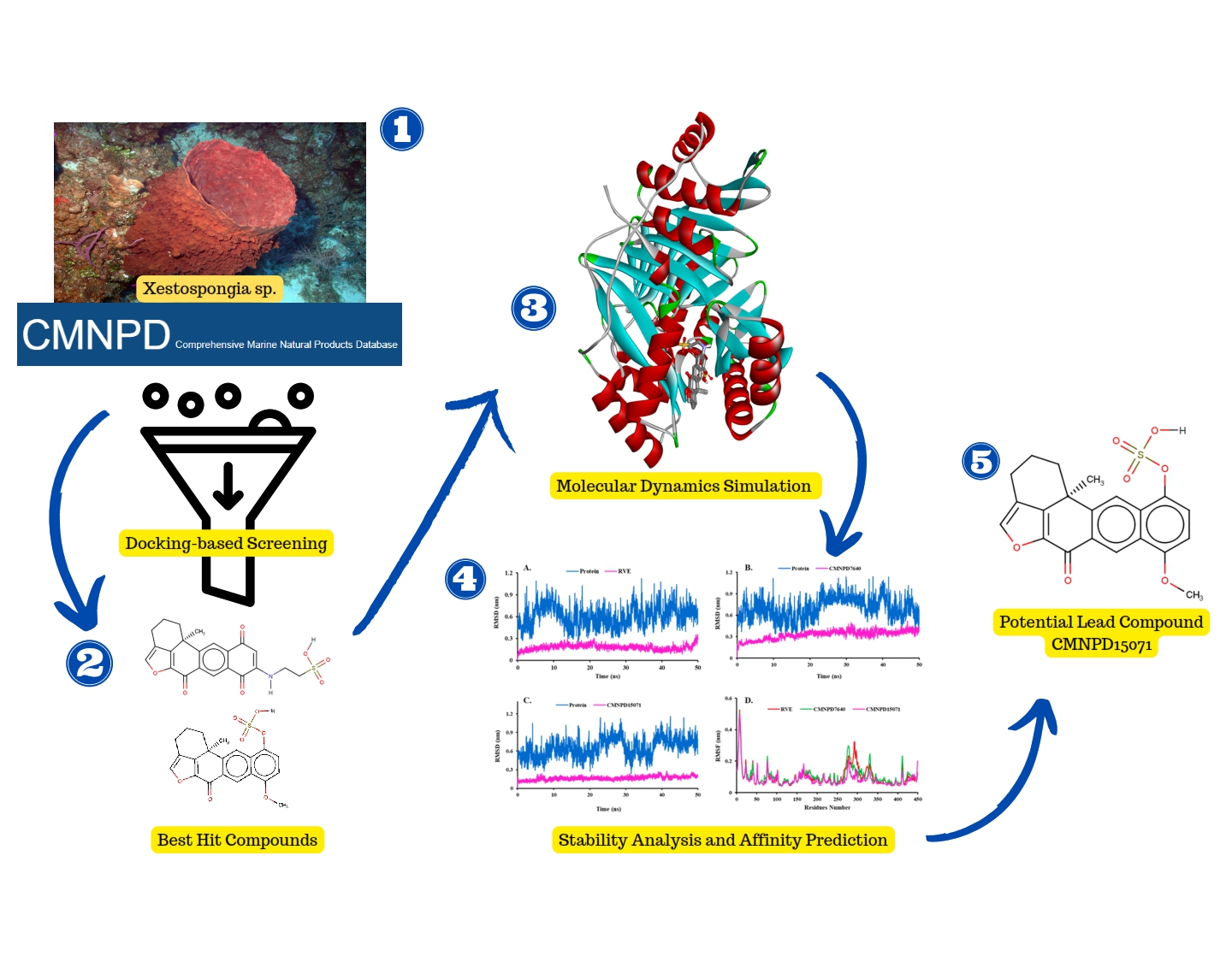
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) remains the leading cause of infection, with a significant fatality rate, owing primarily to drug resistance. MTB contains the enzyme salicylate synthase, which regulates mycobactin production to bind iron ions from the host cell, facilitating the bacteria to grow and reproduce. This study investigates the potential of marine sponges to inhibit the MTB salicylate synthase by exploiting a computational approach combining molecular docking and dynamics simulations. Forty-six compounds from Xestospongia sp. were chosen from the Marine Natural Products database. The docking results selected four compounds (CMNPD15071, CMNPD7640, CMNPD26706, and CMNPD7639) from this sponge, which provide more negative binding energy than their inhibitors (RVE). After reclassifying their interactions, such as hydrophobic and hydrogen bonds, CMNPD15071 (Sulfuric acid mono-(8-methoxy-12b-methyl-6-oxo-2,3,6,12b-tetrahydro-1H-5-oxa-benzo[k]acephenanthrylen-11-yl) ester) and CMNPD7640 (secoadociaquinone B) performed molecular dynamics simulations to assess their stability. These two compounds show a promising stability profile compared to RVE based on RMSD, RMSF, SASA, and gyration analysis. Furthermore, the binding affinity prediction of these two compounds using the MM/GBSA calculation method reveals that CMNPD15071 (-38.48 kJ/mol) had the highest affinity for binding to MTB salicylate synthase compared to RVE (-35.36 kJ/mol) and CMNPD7640 (-26.03 kJ/mol). These findings demonstrate that compounds from Xestospongia sp. can block MTB mycobactin biosynthesis by inhibiting salicylate synthase.
Full text article
References
2. Delghandi MR, El-Matbouli M, Menanteau-Ledouble S. Mycobacteriosis and Infections with Non-tuberculous Mycobacteria in Aquatic Organisms: A Review. Microorganisms. 2020;(8):1368–86. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8091368; PMCID: PMC7564596; PMID: 32906655
3. Chandra P, Grigsby SJ, Philips JA. Immune evasion and provocation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2022;20(12):750–66. DOI: 10.1038/s41579-022-00763-4; PMCID: PMC9310001;PMID: 35879556
4. Pai M, Behr MA, Dowdy D, Dheda K, Divangahi M, Boehme CC, Ginsberg A, et al. Tuberculosis. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2016;2:16076. DOI: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.76; PMID: 27784885
5. Avoi R, Liaw YC. Tuberculosis Death Epidemiology and Its Associated Risk Factors in Sabah, Malaysia. Int J of Envir Res and Pub. 2021;18(18):9740. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18189740; PMCID: PMC8470141; PMID: 34574665
6. Seung KJ, Keshavjee S, Rich ML. Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015;5(9):a017863. DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a017863; PMCID: PMC4561400; PMID: 25918181
7. Miethke M, Pieroni M, Weber T, Brönstrup M, Hammann P, Halby L, et al. Towards the sustainable discovery and development of new antibiotics. Nat Rev Chem. 2021;5(10):726–49. DOI: 10.1038/s41570-021-00313-1; PMCID: PMC8374425; PMID: 34426795
8. Mori M, Stelitano G, Griego A, Chiarelli LR, Cazzaniga G, Gelain A, et al. Synthesis and Assessment of the In Vitro and Ex Vivo Activity of Salicylate Synthase (Mbti) Inhibitors as New Candidates for the Treatment of Mycobacterial Infections. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15(8):992–1012. DOI: 10.3390/ph15080992; PMCID: PMC9413995; PMID: 36015139
9. Liu Z, Liu F, Aldrich CC. Stereocontrolled Synthesis of a Potential Transition-State Inhibitor of the Salicylate Synthase MbtI from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Org Chem. 2015;80(13):6545–52. DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b00455; PMCID: PMC4667787; PMID: 26035083
10. Zhang L, Hendrickson RC, Meikle V, Lefkowitz EJ, Ioerger TR, Niederweis M. Comprehensive analysis of iron utilization by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. PLOS Pathog. 2020;16(2):e1008337. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008337; PMCID: PMC7058343; PMID: 32069330
11. Cloete R, Oppon E, Murungi E, Schubert WD, Christoffels A. Resistance related metabolic pathways for drug target identification in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016;17:75. DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-0898-8; PMCID: PMC4745158; PMID: 26856535
12. Chiarelli LR, Mori M, Barlocco D, Beretta G, Gelain A, Pini E, et al. Discovery and development of novel salicylate synthase (MbtI) furanic inhibitors as antitubercular agents. Eur J Med Chem. 2018;155:754–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.06.033; PMID: 29940465
13. Chiarelli LR, Mori M, Beretta G, Gelain A, Pini E, Sammartino JC, et al. New insight into structure-activity of furan-based salicylate synthase (MbtI) inhibitors as potential antitubercular agents. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2019;34(1):823–8. DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2019.1589462; PMCID: PMC6427685; PMID: 30889995
14. Pini E, Poli G, Tuccinardi T, Chiarelli LR, Mori M, Gelain A, et al. New Chromane-Based Derivatives as Inhibitors of Mycobacterium tuberculosis Salicylate Synthase (MbtI): Preliminary Biological Evaluation and Molecular Modeling Studies. Molecules. 2018;23(7):1506. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071506; PMCID: PMC6099841; PMID: 29933627
15. Karthikeyan A, Joseph A, Nair BG. Promising bioactive compounds from the marine environment and their potential effects on various diseases. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2022;20(1):14. DOI: 10.1186/s43141-021-00290-4; PMCID: PMC8790952; PMID: 35080679
16. Pujiastuti DY, Amin MNG, Alamsjah MA, Hsu JL. Marine Organisms as Potential Sources of Bioactive Peptides that Inhibit the Activity of Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme: A Review. Molecules. 2019;(24):2541. DOI: 10.3390/molecules24142541; PMCID: PMC6680877; PMID: 31336853
17. Yamazaki H. Exploration of marine natural resources in Indonesia and development of efficient strategies for the production of microbial halogenated metabolites. J Nat Med. 2022;76(1):1–19. DOI: 10.1007/s11418-021-01557-3; PMCID: PMC8732978; PMID: 34415546
18. Swantara MD, Rita WS, Suartha N, Agustina KK. Anticancer activities of toxic isolate of Xestospongia testudinaria sponge. Vet World. 2019;12(9):1434–40. DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2019.1434-1440; PMCID: PMC6813599; PMID: 31749578
19. Chi G, Manos-Turvey A, O’Connor PD, Johnston JM, Evans GL, Baker EN, et al. Implications of Binding Mode and Active Site Flexibility for Inhibitor Potency against the Salicylate Synthase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochemistry. 2012;51(24):4868–79. DOI: 10.1021/bi3002067; PMID: 22607697
20. Arba M, Arfan, Trisnawati A, Kurniawati D. Pemodelan Farmakofor untuk Identifikasi Inhibitor Heat Shock Proteins-90 (HSP-90). J Farmasi Galenika Galenika J Pharm. 2020;6(2):229–36. DOI: 10.22487/j24428744.2020.v6.i2.15036
21. Morris GM, Huey R, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, et al. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009;30(16):2785-91. DOI: 10.1002/jcc.21256; PMCID: PMC2760638; PMID: 19399780
22. Lyu C, Chen T, Qiang B, Liu N, Wang H, Zhang L, Liu Z. CMNPD: a comprehensive marine natural products database towards facilitating drug discovery from the ocean. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D509–15. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa763; PMCID: PMC7779072; PMID: 32986829
23. O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform. 2011;3:33. DOI: 10.1186/1758-2946-3-33; PMCID: PMC3198950; PMID: 21982300
24. Morris GM, Huey R, Olson AJ. Using AutoDock for ligand-receptor docking. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2008;Ch8:Unit 8.14 DOI: 10.1002/0471250953.bi0814s24; PMID: 19085980
25. Arfan A, Muliadi R, Malina R, Trinovitasari N, Asnawi A. Docking and Dynamics Studies: Identifying the Binding Ability of Quercetin Analogs to the ADP-Ribose Phosphatase of SARS CoV-2. J Kartika Kimia. 2022;5(2):145–51. DOI: 10.26874/jkk.v5i2.143
26. Kohnke B, Kutzner C, Grubmüller H. A GPU-Accelerated Fast Multipole Method for GROMACS: Performance and Accuracy. J Chem Theory Comput. 2020;16(11):6938–49. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.0c00744; PMCID: PMC7660746; PMID: 33084336
27. Petrov D, Zagrovic B. Are current atomistic force fields accurate enough to study proteins in crowded environments? PLoS Comput Biol. 2014;10(5):e1003638. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003638; PMCID: PMC4031056; PMID: 24854339
28. Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem. 2004;25(9):1157–74. DOI: 10.1002/jcc.20035; PMID: 15116359
29. da Silva AWS, Vranken WF. ACPYPE - AnteChamber PYthon Parser interfacE. BMC Res Notes. 2012;5(367):367. DOI: 10.1186/1756-0500-5-367; PMCID: PMC3461484; PMID: 22824207
30. Asnawi A, Febrina E, Aligita W, Yuliantini A, Arfan A. Penambatan Molekul dan Dinamika Molekul beberapa Fitokimia dari Acalypha Indica L. sebagai Inhibitor Matriks Metalloproteinase9. J Sains Farmasi Klinis. 2023;10(1):69–77. DOI: 10.25077/jsfk.10.1.69-77.2023
31. Aman LO, Sihaloho M, Arfan A. Pencarian Inhibitor DYRK2 dari Database Bahan Alam Zinc15: Analisis Farmakofor, Simulasi Docking dan Dinamika Molekuler. J Sains Farmasi Klinis. 2023;10(1):100–13. DOI: 10.25077/jsfk.10.1.100-113.2023
32. Asnawi A, Aman LO, Yuliantini A, Febrina E. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Studies: Screening Phytochemicals of Acalypha Indica against Braf Kinase Receptors for Potential use in Melanocytic Tumours. Rasāyan J Chem. 2022;15(2):1352–61. DOI: 10.31788/RJC.2022.1526769
33. Meng XY, Zhang HX, Mezei M, Cui M. Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2011;7(2):146-57. DOI: 10.2174/157340911795677602; PMCID: PMC3151162; PMID: 21534921
34. Rampogu S, Lee G, Park JS, Lee KW, Kim MO. Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations Discover Curcumin Analogue as a Plausible Dual Inhibitor for SARS-CoV-2. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1771. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23031771; PMCID: PMC8836015; PMID: 35163692
35. Citra SNAL, Arfan A, Alroem A, Bande LS, Irnawati I, Arba M. Docking-based workflow and ADME prediction of some compounds in Curcuma longa and Andrographis paniculata as polymerase PA-PB1 inhibitors of influenza A/H5N1 virus. J Res Pharm. 2023;27(1):221–31. DOI: 10.29228/jrp.305
36. Du X, Li Y, Xia YL, Ai SM, Liang J, Sang P, et al. Insights into Protein-Ligand Interactions: Mechanisms, Models, and Methods. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(2):144. DOI: 10.3390/ijms17020144; PMCID: PMC4783878; PMID: 26821017
37. Ghahremanian S, Rashidi MM, Raeisi K, Toghraie D. Molecular dynamics simulation approach for discovering potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2: A structural review. J Mol Liq. 2022;354:118901. DOI: 10.1016/j.molliq.2022.118901; PMCID: PMC8916543; PMID: 35309259
38. Rakhsit G, Biswas A, Jayaprakash V. In Silico Drug Repurposing Studies for the Discovery of Novel Salicyl-AMP Ligase (MbtA)Inhibitors. Pathogens. 2023;12(12):1433. DOI: 10.3390/pathogens12121433; PMCID: PMC10745912; PMID: 38133316
39. Ali SA, Hassan MI, Islam A, Ahmad F. A review of methods available to estimate solvent-accessible surface areas of soluble proteins in the folded and unfolded states. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2014;15(5):456-76. DOI: 10.2174/1389203715666140327114232; PMID: 24678666
40. Genheden S, Ryde U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA methods to estimate ligand-binding affinities. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2015;10(5):449-61. DOI: 10.1517/17460441.2015.1032936; PMCID: PMC4487606; PMID: 25835573
41. Li Z, Chan KC, Nickels JD, Cheng X. Electrostatic Contributions to the Binding Free Energy of Nicotine to the Acetylcholine Binding Protein. J Phys Chem B. 2022;126(43):8669-79. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c04641; PMCID: PMC10056799; PMID: 36260486
42. Arfan A, Muliadi R, Rayani R. Eksplorasi Senyawa Penghambat Enzim Salisilat Sintase dari Mycobacterium tuberculosis melalui Studi Penambatan Molekul dan Prediksi Sifat ADME. Lansau J Ilmu Kefarmasian. 2023;1(1):77-88. DOI: 10.33772/lansau.v1i1.9
43. Izadi S, Aguilar B, Onufriev AV. Protein-Ligand Electrostatic Binding Free Energies from Explicit and Implicit Solvation. J Chem Theory Comput. 2015;11(9):4450-9. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.5b00483; PMCID: PMC5217485; PMID: 26575935
44. Pantsar T, Poso A. Binding Affinity via Docking: Fact and Fiction. Molecules. 2018;23(8):1899. DOI: 10.3390/molecules23081899; PMCID: PMC6222344; PMID: 30061498
45. Roth CM, Neal BL, Lenhoff AM. Van der Waals interactions involving proteins. Biophys J. 1996;70(2):977-87. DOI: 10.1016/s0006-3495(96)79641-8; PMCID: PMC1224998; PMID: 8789115
Authors
Copyright (c) 2024 Arfan Arfan, Aiyi Asnawi, La Ode Aman

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.