Antibacterial Activity and Bioautography Test of Ethanol Extract of Kitolod (Isotoma longiflora (L.) C. Presl.) Leaves against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhi using Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction
Abstract
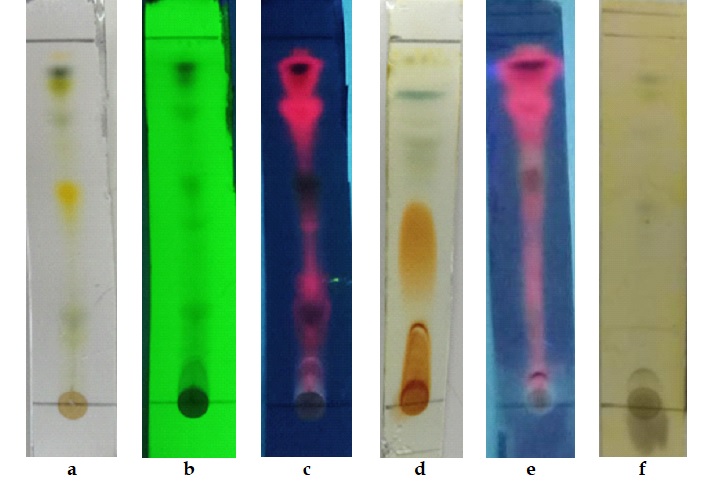
Isotoma longiflora (L.) C. Presl. (Kitolod) is recognized for its potential as a natural antibacterial agent, with prior studies on its leaf extracts demonstrating inhibitory effects against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhi. This research aimed to investigate the antibacterial efficacy of I. longiflora leaf ethanol extracts, determine their phytochemical composition, and identify the active compounds responsible for the observed antibacterial activity. Extracts were prepared using ultrasonic-assisted extraction (34°C, 38 Hz, 40 minutes) with 70%, 85%, and 96% ethanol solvents. Antibacterial activity was assessed using the well diffusion method at concentrations of 40%, 60%, and 80%, against positive controls (ampicillin 10 µg and chloramphenicol 30 µg) and a negative control (100% DMSO). The highest activity against S. aureus was demonstrated by the 96% ethanol extract at 80% concentration, yielding an average inhibition zone of 13.3 ± 1.2 mm against S. typhi. The 85% ethanol extract at a concentration of 80% was most effective, with an inhibition zone of 9.5 ± 0.7 mm. Phytochemical screening confirmed the presence of alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, and phenolics in both the 85% and 96% ethanol extracts. However, the attempt to identify the specific active antibacterial compounds via the contact bioautography method yielded negative results, suggesting the need for further isolation and identification studies.
Full text article
References
2. Nazir A, Nazir A, Zuhair V, Aman S, Sadiq SUR, Hasan AH, et al. The Global Challenge of Antimicrobial Resistance: Mechanisms, Case Studies, and Mitigation Approaches. Health Sci Rep. 2025;8(7):e71077. DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.71077; PMCID: PMC12284435; PMID: 40704322
3. Kumar P, Kumar D, Gautam V, Singh S, Pratama MRF. Antimicrobial Resistance a Global Burden - Mechanisms, Current Insights, and Future Directions. Bull Pharm Sci Assiut Univ. 2025;48(1):523-45. DOI: 10.21608/bfsa.2024.310197.2228
4. Wardani TS, Nisa TC, Artini KS. Antibacterial Activity Test of N-Hexan, Ethyl Acetate and Water from Ethanol Extract of Kitolod Leaf (Isotoma Longiflora (L.) C. Presl.) AGAINST Staphylococcus Aureus ATCC 25923. Proceed Int Conf Nurs Health Sci. 2022;3(1):9-16. DOI: 10.37287/picnhs.v3i1.984
5. Eff ARY. Uji Sitotoksik Ekstrak Etanol 50% Daun Kitolod (Isotoma longiflora (L.) Presl.) terhadap Sel Kanker Serviks (Ca Ski Cell Line) secara In- Vitro. Farmasains J Ilmiah Ilmu Kefarmasian. 2016;3(1):7-12.
6. Anjelina SH. Antibacterial Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Kitolod (Hippobromalongiflora) Leaf Against Staphylococcus aureus and Salmonella typhi. Asian J Pharm Res Dev. 2020;8(1):52–4. DOI: 10.22270/ajprd.v8i1.660
7. Angganawati RT, Nisa TC. Uji Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kitolod (Isotoma longiflora (L.) C. Presl.) terhadap bakteri Staphylococcus aureus dengan Kontrol Antibiotik Ofloxacin. J Farmasindo J Penelitian Pengabdian Masyarakat. 2019;3(1):5–8. DOI: 10.46808/farmasindo.v3i1.14
8. Shen L, Pang S, Zhong M, Sun Y, Qayum A, Liu Y, et al. A comprehensive review of ultrasonic assisted extraction (UAE) for bioactive components: Principles, advantages, equipment, and combined technologies. Ultrason Sonochem. 2023;101:106646. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2023.106646; PMCID: PMC10594638; PMID: 37862945
9. Mubarak F, Sartini S, Purnawanti D. Effect of Ethanol Concentration on Antibacterial Activity of Bligo Fruit Extract (Benincasa hispida Thunb) to Salmonella typhi. Indones J Pharm Sci Technol. 2018;5(3):76-81. DOI: 10.24198/ijpst.v5i3.16444
10. Phuyal N, Jha PK, Raturi PP, Rajbhandary S. In Vitro Antibacterial Activities of Methanolic Extracts of Fruits, Seeds, and Bark of Zanthoxylum armatum DC. J Trop Med. 2020;2020:2803063. DOI: 10.1155/2020/2803063; PMCID: PMC7292994; PMID: 32565829
11. Maheshwaran L, Nadarajah L, Senadeera SPNN, Ranaweera CB, Chandana AK, Pathirana RN. Phytochemical Testing Methodologies and Principles for Preliminary Screening/ Qualitative Testing. Asian Plant Res J. 2024;12(5):11-38. DOI: 10.9734/aprj/2024/v12i5267
12. Kowalska T, Sajewicz M. Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC) in the Screening of Botanicals-Its Versatile Potential and Selected Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(19):6607. DOI: 10.3390/molecules27196607; PMCID: PMC9572063; PMID: 36235143
13. Kancherla N, Dhakshinamoothi A, Chitra K, Komaram RB. Preliminary Analysis of Phytoconstituents and Evaluation of Anthelminthic Property of Cayratia auriculata (In Vitro). Maedica. 2019;14(4):350-6. DOI: 10.26574/maedica.2019.14.4.350; PMCID: PMC7035446; PMID: 32153665
14. Spangenberg B, Poole CF, Weins C. Quantitative Thin-Layer Chromatography: A Practical Survey. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; 2011. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-10729-0
15. Tock MLA, Combrinck S, Kamatou G, Chen W, Vuuren SV, Viljoen A. Antibacterial Screening, Biochemometric and Bioautographic Evaluation of the Non-Volatile Bioactive Components of Three Indigenous South African Salvia Species. Antibiotics. 2022;11(7):901. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics11070901; PMCID: PMC9312202; PMID: 35884155
16. Armonavičius D, Maruška A, Jakštys B, Stankevičius M, Drevinskas T, Bimbiraitė-Survilienė K, et al. Evaluation of the Anticancer Activity of Medicinal Plants Predominantly Accumulating Ellagic Acid Compounds. Antioxidants. 2025;14(11):1339. DOI: 10.3390/antiox14111339; PMCID: PMC12649554; PMID: 41300496
17. Sunnah I, Dianingati RS, Wulandari AR. Optimasi Pelarut terhadap Parameter Spesifik Ekstrak Kitolod (Isotoma longiflora). Generics J Res Pharm. 2021;1(1):10–5. DOI: 10.14710/genres.v1i1.9847
18. Awwaliyah R, Muslikh FA, Abada I, Megawati DS, Inayatillah R, Wijaya D, et al. Aktivitas Penyembuhan Luka Formulasi Salep Ekstrak Etanol Daun Kitolod (Isotoma longiflora) pada Mencit (Mus musculus). J Dunia Farmasi. 2023;7(2):105-15. DOI: 10.33085/jdf.v7i2.5425
19. Ariestanti DM, Mun'im A, Hartrianti P, Nadia B, Chriscensia E, Rattu SA, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE) of Javanese turmeric rhizomes using natural deep eutectic solvents (NADES): Screening, optimization, and in vitro cytotoxicity evaluation. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025;114:107271. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2025.107271; PMCID: PMC11872070; PMID: 39955874
20. Hossain TJ. Methods for screening and evaluation of antimicrobial activity: A review of protocols, advantages, and limitations. Eur J Microbiol Immunol. 2024;14(2):97-115. DOI: 10.1556/1886.2024.00035; PMCID: PMC11097785; PMID: 38648108
21. Nurafifah OA, Lantang D, Pratiwi RD, Dewi K, Bakri NF. Antibacterial Activity of Kitolod (Isotoma Longiflora L.) Herb Extract and Fractions Against the Growth of Dental Carises Causing Bacteria Streptococcus Mutans. Int J Pharm Bio Med Sci. 2025;5(4):227-32. DOI: 10.47191/ijpbms/v5-i4-02
22. Ahmad R, Amiruddin R, Arsin A, Stang S, Ishak H, Wahiduddin, et al. Phytochemical Screening and Antibacterial Activity Test of Ethanol Extract of Durian (Durio Zibethinus murr.) Soya Varieties Against Pathogen Bacteria Escherichia Coli in Raw Drinking Water. Pharmacogn J. 2024;16(4):933-41. DOI: 10.5530/pj.2024.16.151
23. Kefayati Z, Motamed SM, Shojaii A, Noori M, Ghods R. Antioxidant Activity and Phenolic and Flavonoid Contents of the Extract and Subfractions of Euphorbia splendida Mobayen. Pharmacogn Res. 2017;9(4):362-5. DOI: 10.4103/pr.pr_12_17; PMCID: PMC5717788; PMID: 29263629
24. Godlewska K, Pacyga P, Najda A, Michalak I. Investigation of Chemical Constituents and Antioxidant Activity of Biologically Active Plant-Derived Natural Products. Molecules. 2023;28(14):5572. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28145572; PMCID: PMC10384900; PMID: 37513443
25. Wang M, Zhang Y, Wang R, Wang Z, Yang B, Kuang H. An Evolving Technology That Integrates Classical Methods with Continuous Technological Developments: Thin-Layer Chromatography Bioautography. Molecules. 2021;26(15):4647. DOI: 10.3390/molecules26154647; PMCID: PMC8347725; PMID: 34361800
26. Urma SRA, Ahmed SF, Imran MAS, Akhand MRN, Khan MMH. Antimicrobial Activity of Tea and Agarwood Leaf Extracts Against Multidrug-Resistant Microbes. Biomed Res Int. 2024;2024:5595575. DOI: 10.1155/bmri/5595575; PMCID: PMC11671646; PMID: 39734496
27. Zhang Z, Cao M, Shang Z, Xu J, Chen X, Zhu Z, et al. Research Progress on the Antibacterial Activity of Natural Flavonoids. Antibiotics. 2025;14(4):334. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14040334; PMCID: PMC12023951; PMID: 40298463
28. Buchmann D, Schwabe M, Weiss R, Kuss AW, Schaufler K, Schlüter R, et al. Natural phenolic compounds as biofilm inhibitors of multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli - the role of similar biological processes despite structural diversity. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1232039. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1232039; PMCID: PMC10507321; PMID: 37731930
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Fajrin Ahidannisa Yuhdi, Ika Trisharyanti Dian Kusumowati

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.