A Pre-Post Survey Analysis on Pharmacy Students' Perceptions of Pharmacist Roles in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Abstract
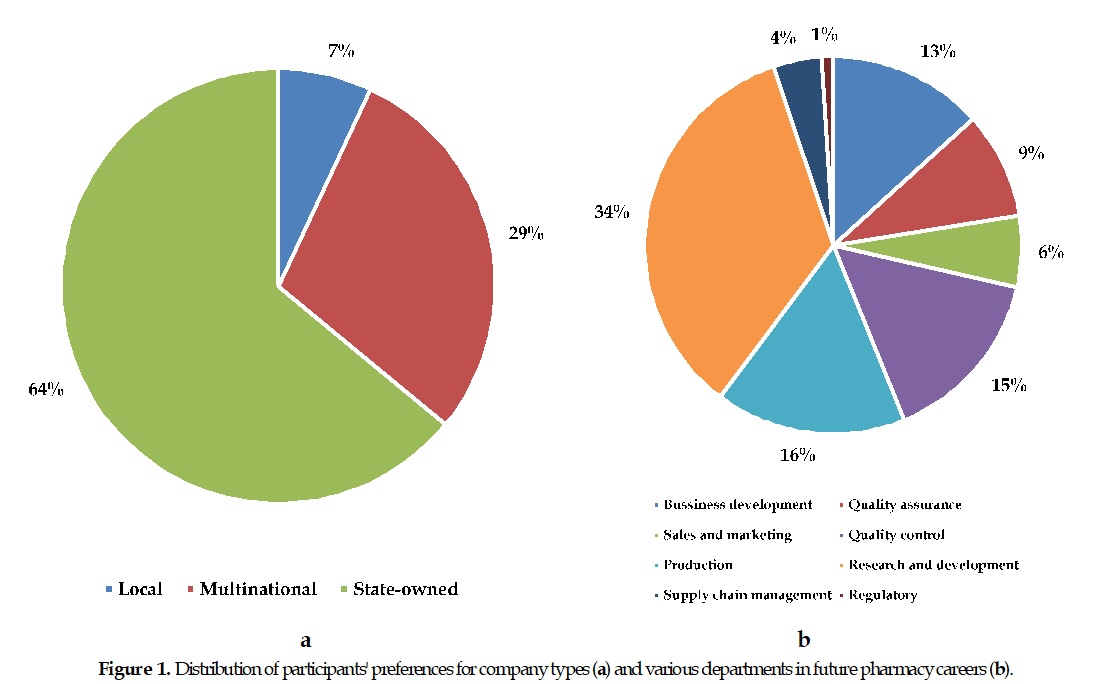
The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing rapid evolution, characterized by a complex regulatory landscape and the need for diverse skill sets. This study aimed to assess pharmacy students’ perceptions of the pharmaceutical industry and the impact of a dedicated seminar on their career aspirations and knowledge. A pre-post online survey was administered to 55 undergraduate pharmacy students at the National Pharmacy Seminar 2024, hosted by Jakarta Global University. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test (p ≤0.05). Results indicate a strong preference for careers in state-owned pharmaceutical companies (63.6%) and research and development departments (34%). The seminar significantly enhanced participants’ understanding of pharmacists’ roles, industry complexities, drug development challenges, and regulatory requirements. Notably, 93% of participants reported that the seminar met their expectations and provided valuable insights for future career exploration. These findings underscore the importance of educational interventions in shaping pharmacy students’ career trajectories and aligning their knowledge with the dynamic pharmaceutical industry.
Full text article
References
2. O’Dwyer M, Filieri R, O’Malley L. Establishing successful university–industry collaborations: barriers and enablers deconstructed. J Technol Transf. 2023;48(3):900–31. DOI: 10.1007/s10961-022-09932-2
3. Khurshid F, Alharbi F, Almohydib A, Malik SI, Al-Omar HA, Alsultan MS, et al. Preparatory Year Students’ Perception of Pharmacy Profession as a Career Choice: A Cross-Sectional Study. Braz J Pharm Sci. 2023;59:e21476. DOI: 10.1590/s2175-97902023e21476
4. Wong WJ, Lee RFS, Chong LY, Lee SWH, Lau WM. Work readiness of pharmacy graduates: An exploratory study. Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2023;13:100389. DOI: 10.1016/j.rcsop.2023.100389; PMCID: PMC10776422; PMID: 38204886
5. Lysetty S, Kannan SK, Naha A, Nayak UY, Ligade V. Design of Skill Enhancement Module for Pharmacy Students - Need of the Hour. Ind J Pharm Educ Res. 2022;56(3):618–27. DOI: 10.5530/ijper.56.3.110
6. Etukakpan A, Uzman N, Ozer O, Tofade T, Leite SN, Joda A, et al. Transforming pharmaceutical education: A needs-based global analysis for policy development. Explor Res Clin Soc Pharm. 2023;9:100234. DOI:10.1016/j.rcsop.2023.100234; PMCID: PMC9981992; PMID: 36876147
7. Nouri AI, Hassali MA, Hashmi FK. Contribution of pharmacy education to pharmaceutical research and development: critical insights from educators. Perspect Public Health. 2020;140(1):62-6. DOI: 10.1177/1757913919832927; PMID: 31165671
8. de la Peña I, Knecht K, Gavaza P. Pharmacy Students’ Perception of an Elective Course on Evidence-based Learning Strategies. Am J Pharm Educ. 2021;85(2):8232. DOI: 10.5688/ajpe8232; PMCID: PMC7926278; PMID: 34283741
9. Menon UK, Gopalakrishnan S, Unni CSN, Ramachandran R, Poornima B, Sasidharan A, et al. Pilot of a questionnaire study regarding perception of undergraduate medical students towards online classes: Process and perspectives. J Familiy Med Prim Care. 2021;10(5):2016-21. DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_2141_20; PMCID: PMC8208202; PMID: 34195141
10. Skipper TL. What makes the first-year seminar high impact? An exploration of effective educational practices. (Research Reports No. 7). Columbia (SC): National Resource Center for The First-Year Experience and Students in Transition University of South Carolina; 2017.
11. Othman MI, Najib MNM, Sulaiman S, Khalid MIHA, Zamri MID, Shakri MSM, et al. Pathway to Success: Exploring Students’ Perspectives on Career Aspirations in Pharmacy. J Intelek. 2024;19(1):103-14. DOI: 10.24191/ji.v19i1.24556
12. Romanelli F, Bird E, Fink J. Development and evaluation of an introduction to pharmacy seminar for faculty, staff, and graduate students. Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2009;1(2):98-102. DOI: 10.1016/j.cptl.2009.10.004
13. Al’Adawi SSA. Exploring the Effectiveness of Implementing Seminars as a Teaching and an Assessment Method in a Children’s Literature Course. Engl Lang Teach. 2017;10(11):1-14. DOI: 10.5539/elt.v10n11p1
14. Cameron C, Carroll K, Forbes A, Luca X, Alamer AA, Fazel MT. A Cross-Sectional Survey Study of Student Pharmacists’ Career Interests. J Pharm Pract. 2024;37(4):906-15. DOI: 10.1177/08971900231198926; PMID: 37655622
15. Almeman A. The digital transformation in pharmacy: embracing online platforms and the cosmeceutical paradigm shift. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024;43(1):60. DOI: 10.1186/s41043-024-00550-2; PMCID: PMC11080122; PMID: 38720390
16. Kamath S, Soo B, Mill D, Johnson J, Page AT. Who would be a pharmacist? A national representative cross-sectional survey of pharmacists and students to explore personality traits and associations with job satisfaction and career outlook. Int J Pharm Pract. 2023;31(3):328–36. DOI: 10.1093/ijpp/riad012; PMID: 36933196
17. Joshi G, Kabra A, Goutam N, Sharma A. An Overview on Patient-Centered Clinical Services. Borneo J Pharm. 2021;4(2):157-70. DOI: 10.33084/bjop.v4i2.1978
18. Ilardo ML, Speciale A. The Community Pharmacist: Perceived Barriers and Patient-Centered Care Communication. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(2):536. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17020536; PMCID: PMC7013626; PMID: 31952127
19. Afanasenko OV, Nizhenkovska IV, Holovchenko OI, Glushachenko OO. Technology-enhanced constructivist learning environment for pharmacy students. Pharm Educ. 2022;22(1):778–87. DOI: 10.46542/pe.2022.221.778787
20. Hall K, Musing E, Miller DA, Tsdale JE. Experiential training for pharmacy students: time for a new approach. Can J Hosp Pharm. 2012;65(4):285-93. DOI: 10.4212/cjhp.v65i4.1159; PMCID: PMC3420851; PMID: 22919106
21. Suwannaprom P, Suttajit S, Eakanunkul S, Supapaan T, Kessomboon N, Udomaksorn K, et al. Development of pharmacy competency framework for the changing demands of Thailand's pharmaceutical and health services. Pharm Pract. 2020;18(4):2141. DOI: 10.18549/pharmpract.2020.4.2141; PMCID: PMC7732214; PMID: 33343773
22. Kolb DA. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development. New Jersey: Prentice Hall; 1984.
23. Golikova NS, Prisyazhnaya NV, Tarasov VV. Improvement of pharmaceutical education in Russia: survey of students, university teachers and specialists in pharmaceutical industry. Med Technol Assess Choice. 2023;4:85. DOI: 10.17116/medtech20234504185
24. Tang Y, Liu Y, Liao H, Yuan Y, Jiang Q. Current career situations of Chinese pharmacovigilance professionals working for pharmaceutical companies: an exploratory survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2023;23(1):152. DOI: 10.1186/s12913-023-09089-0; PMCID: PMC9926404; PMID: 36788574
25. Vasileiou K, Barnett J, Thorpe S, Young T. Characterising and justifying sample size sufficiency in interview-based studies: systematic analysis of qualitative health research over a 15-year period. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18(1):148. DOI: 10.1186/s12874-018-0594-7; PMCID: PMC6249736; PMID: 30463515
Authors
Copyright (c) 2024 Anugerah Budipratama Adina, Alhara Yuwanda, Rizky Farmasita Budiastuti, Nopratilova Nopratilova, Eddy Yusuf, Suk Fei Tan, Saeid Mezail Mawazi, Amelia Herli

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.