Wound Healing Activity of Gel Nanoparticles of Rhaphidophora pinnnata Leaves Extract in Male Rats
Abstract
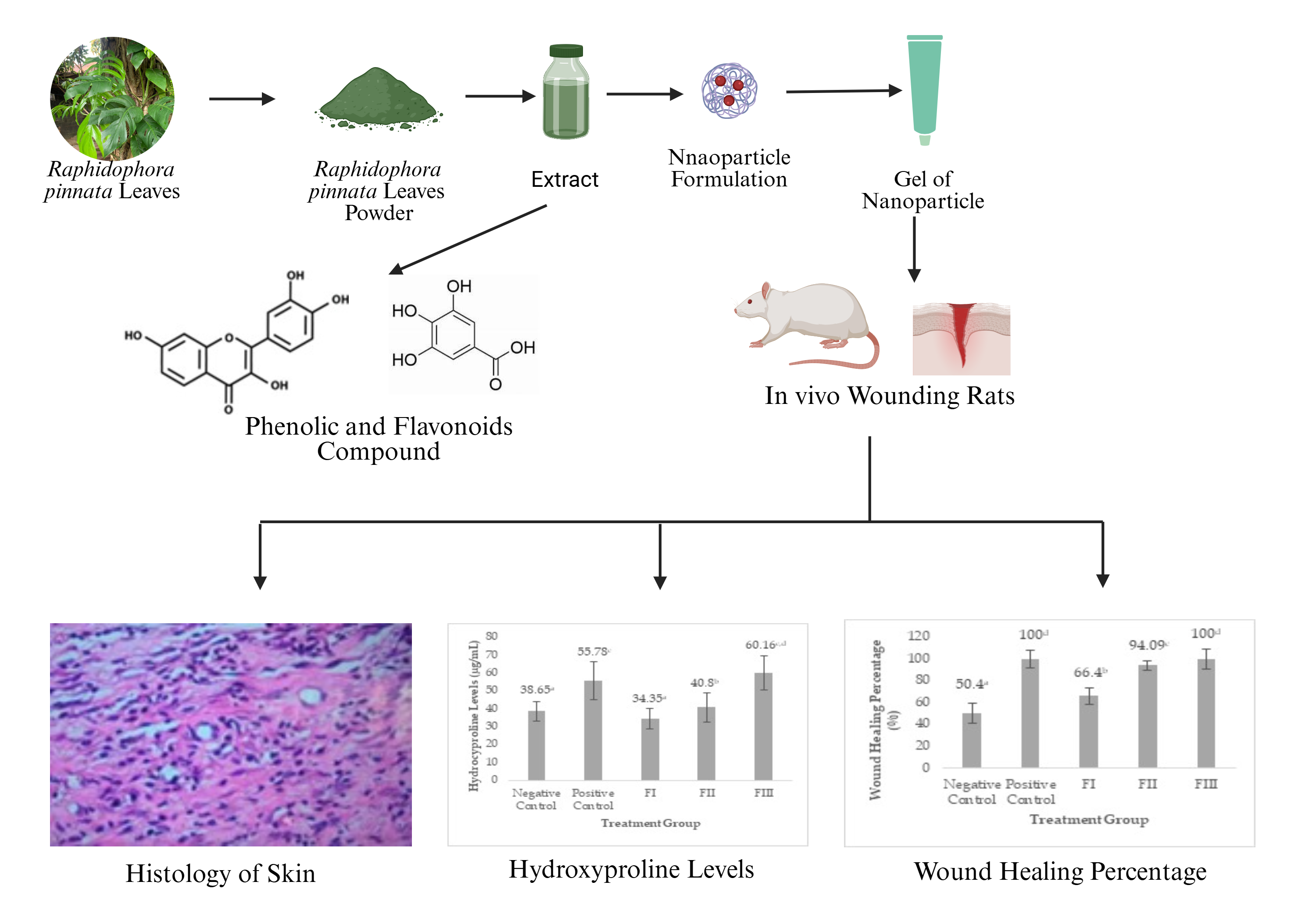
Rhaphidophora pinnata, a plant traditionally recognized for its wound-healing properties, contains active compounds such as megastigmane glycosides and damascenone, known for their anti-inflammatory effects. To enhance efficacy and user comfort, this study focused on developing an R. pinnata leaf extract nanoparticle gel. Previous research from our group highlighted the significant wound-healing potential of a conventional R. pinnata gel. This present study aimed to evaluate the wound-healing efficacy of a novel R. pinnata nanoparticle gel in male Wistar rats, specifically investigating the impact of nanotechnology application. Nanoparticles were successfully formulated via the ionic gelation method, utilizing 0.250 g of R. pinnata extract, 0.1% chitosan, 0.2% sodium tripolyphosphate, and 0.5% Tween 80. Characterization revealed an average nanoparticle size of 165.70±42.76 nm with a zeta potential of 22.0±1.83 mV. The wound-healing efficacy was assessed across five treatment groups: a positive control (Bioplasenton®), a plain gel base (Formula 0), and nanoparticle gels at 0.5% (Formula I), 1% (Formula II), and 1.5% (Formula III) extract concentrations. Statistical analysis using one-way ANOVA (p <0.05) demonstrated a significant difference in incision wound healing across the groups. Formula III, containing 1.5% R. pinnata nanoparticle extract, exhibited the most superior wound-healing effect, achieving 100% inhibition by day 14, elevated hydroxyproline levels (59 µg/mL), and histologically confirmed excellent skin tissue repair. Formulas II and I followed in efficacy. These compelling findings underscore the significant potential of utilizing nanotechnology in the development of topical preparations for accelerated and effective wound healing.
Full text article
References
2. Kasmadi FS, Rahman H, Rahman AO, Samudra AG, Floris C De. Incision wound healing test ethanolic extract gel from Ekor Naga (Rhaphidophora pinnata (L.f) Schott) leaves in white male rats. Pharmaciana. 2022;12(2):173-80. DOI: 10.12928/pharmaciana.v12i2.22825
3. Pan SP, Pirker T, Kunert O, Kretschmer N, Hummelbrunner S, Latkolik SL, et al. C13 megastigmane derivatives from epipremnum pinnatum: β-damascenone inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and leukocyte adhesion molecules as well as NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:1351. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01351; PMCID: PMC6892967; PMID: 31849641
4. Tarigan BA, Kasmadi FS, Muhaimin. Topical anti-inflammatory effect of Ekor Naga (Rhaphidophora pinnata (L.f) Schott) leaves extract. Pharmaciana. 2021;11(3):303–11. DOI: 10.12928/pharmaciana.v11i3.17617
5. Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem. 2019;12(7):908-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
6. Sharma D, Kanchi S, Bisetty K. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arab J Chem. 2019;12(8):3576-600. DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.11.002
7. Ansari SH, Islam F, Sameem M. Influence of nanotechnology on herbal drugs: A Review. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2012;3(3):142-6. DOI: 10.4103/2231-4040.101006; PMCID: PMC3459443; PMID: 23057000
8. Souto EB, Ribeiro AF, Ferreira MI, Teixeira MC, Shimojo AAM, Soriano JL, et al. New nanotechnologies for the treatment and repair of skin burns infections. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(2):393. DOI: 10.3390/ijms21020393; PMCID: 10.3390/ijms21020393; PMID: 31936277
9. Zeng C, Wei J, Persson MSM, Sarmanova A, Doherty M, Xie D, et al. Relative efficacy and safety of topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials and observational studies. Br J Sports Med. 2018;52(10):642-50. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098043; PMCID: PMC5931249; PMID: 29436380
10. Taha M, Alhakamy NA, Md S, Ahmad MZ, Rizwanullah M, Fatima S, et al. Nanogels as Potential Delivery Vehicles in Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of Phytopharmaceuticals. Plymers. 2022;14(19):4141. DOI: 10.3390/polym14194141; PMCID: PMC9570606; PMID: 36236089
11. Samudra AG, Ramadhani N, Lestari G, Nugroho BH. Formulasi Nanopartikel Kitosan Ekstrak Metanol Alga Laut Coklat (Sargassum hystrix) dengan Metode Gelasi Ionik. J Ilmiah Manuntung. 2021;7(1):92–9. DOI: 10.51352/jim.v7i1.428
12. Samudra AG, Ramadhani N, Pertiwi R, Fitriani D, Sanik F, Burhan A. Antihyperglycemic activity of nanoemulsion of brown algae (Sargassum sp.). Ethanol extract in glucose tolerance test in male mice. Ann Pharm Fr. 2023;81(3):484-91. DOI: 10.1016/j.pharma.2022.11.011; PMID: 36464073
13. Saberi AH, Fang Y, McClements DJ. Effect of glycerol on formation, stability, and properties of vitamin-E enriched nanoemulsions produced using spontaneous emulsification. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2013;411:105-13. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2013.08.041; PMID: 24050638
14. Bhatia S. Nanoparticles Types, Classification, Characterization, Fabrication Methods and Drug Delivery Applications. In: Natural Polymer Drug Delivery Systems. Cham; Springer: 2016. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-41129-3_2
15. Afrinanda R, Ristiawati Y, Islami MS, Pertiwi DV. Extraction, Identification, and Gel Formulation of Mangiferin from Mango (Mangifera indica L.) Leaves Extract. In: Hanani E, Permanasari ED, Sjahid LR, Dwita LP, Viviandhai D, Rindita, editors. Proceedings of the 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development MICH-PhD. Setúbal; SciTePress: 2019. DOI: 10.5220/0008240701380142
16. Builders P, Kabele-Toge B, Builders M, Chindo B, Anwunobi P, Isimi Y. Wound healing potential of formulated extract from hibiscus sabdariffa calyx. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2013;75(1):45-52. DOI: 10.4103/0250-474X.113549; PMCID: PMC3719149; PMID: 23901160
17. Shahtalebi MA, Asghari GR, Rahmani F, Shafiee F, Jahanian-Najafabadi A. Formulation of Herbal Gel of Antirrhinum majus Extract and Evaluation of its Anti- Propionibacterium acne Effects. Adv Biomed Res. 2018;7:53. DOI: 10.4103/abr.abr_99_17; PMCID: PMC5887696; PMID: 29657938
18. Darestani KD, Mirghazanfari SM, Moghaddam KG, Hejazi S. Leech therapy for linear incisional skin-wound healing in rats. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2014;7(4):194-201. DOI: 10.1016/j.jams.2014.01.001; PMID: 25151453
19. Wairata J, Fadlan A, Purnomo AS, Taher M, Ersam T. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant, antidiabetic and antiplasmodial activities of Garcinia forbesii King: A correlation study. Arab J Chem. 2022;15(2):103541. DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103541
20. Hidayah LA, Anggarani MA. Determination of Total Phenolic, Total Flavonoid, and Antioxidant Activity of India Onion Extract. Indones J Chem Sci. 2022;11(2):123-35. DOI: 10.15294/ijcs.v11i2.54610
21. Mizzi L, Chatzitzika C, Gatt R, Valdramidis V. HPLC analysis of phenolic compounds and flavonoids with overlapping peaks. Food Technol Biotechnol. 2020;58(1):12-9. DOI: 10.17113/ftb.58.01.20.6395
22. Li G, Ding K, Qiao Y, Zhang L, Zheng L, Pan T, et al. Flavonoids regulate inflammation and oxidative stress in cancer. Molecules. 2020;58(1):12-9. DOI: 10.3390/molecules25235628; PMCID: PMC7365340; PMID: 32684783
23. Hoang NH, Thanh T Le, Sangpueak R, Treekoon J, Saengchan C, Thepbandit W, et al. Chitosan Nanoparticles-Based Ionic Gelation Method: A Promising Candidate for Plant Disease Management. Polymers. 2022;14(4):662. DOI: 10.3390/polym14040662; PMCID: PMC8876194; PMID: 35215574
24. Bavel NV, Issler T, Pang L, Anikovskiy M, Prenner EJ. A Simple Method for Synthesis of Chitosan Nanoparticles with Ionic Gelation and Homogenization. Molecules. 2023;28(11):4328. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28114328; PMCID: PMC10254159; PMID: 37298804
25. Alehosseini E, Tabarestani HS, Kharazmi MS, Jafari SM. Physicochemical, Thermal, and Morphological Properties of Chitosan Nanoparticles Produced by Ionic Gelation. Foods. 2022;11(23):3841. DOI: 10.3390/foods11233841; PMCID: PMC9736386; PMID: 36496649
26. Popova EV, Zorin IM, Domnina NS, Novikova II, Krasnobaeva IL. Chitosan–Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles: Synthesis by the Ionic Gelation Method, Properties, and Biological Activity. Russ J Gen Chem. 2020;90:1304-11. DOI: 10.1134/S1070363220070178
27. Hoshyar N, Gray S, Han H, Bao G. The effect of nanoparticle size on in vivo pharmacokinetics and cellular interaction. Nanomedicine. 2016;11(6):673-92. DOI: 10.2217/nnm.16.5; PMCID: PMC5561790; PMID: 27003448
28. Raval N, Maheshwari R, Kalyane D, Youngren-Ortiz SR, Chougule MB, Tekade RK. Importance of physicochemical characterization of nanoparticles in pharmaceutical product development. In: Tekade RK, editor. Basic Fundamentals of Drug Delivery. New York; Academic Press: 2019. p. 369-400. DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-817909-3.00010-8
29. Rahmat D, Farida Y, Brylianto AT, Sumarny R, Kumala S. Antidiabetic activity of nanoparticles containing Javanese turmeric rhizome extract: The strategy to change particle size. Int J Appl Pharm. 2020; 12(4):90-3. DOI: 10.22159/jap.2020v12i4.36249
30. Oudih SB, Tahtat D, Khodja AN, Mahlous M, Hammache Y, Guittoum AE, et al. Chitosan nanoparticles with controlled size and zeta potential. Polym Eng Sci. 2023;63(3):1011-21. DOI: 10.1002/pen.26261
31. Soleymanfallah S, Khoshkhoo Z, Hosseini SE, Azizi MH. Preparation, physical properties, and evaluation of antioxidant capacity of aqueous grape extract loaded in chitosan-TPP nanoparticles. Food Sci Nutr. 2022;10(10):3272-81. DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2891
32. Virk P, Awad MA, Saleh Abdu-llah Alsaif S, Hendi AA, Elobeid M, Ortashi K, et al. Green synthesis of Moringa oleifera leaf nanoparticles and an assessment of their therapeutic potential. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2023;35(3):102576. DOI: 10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102576
33. Bhatia S, Shah YA, Al-Harassi A, Jawad M, Khan TS, Koca E, et al. Tuning the structure and physiochemical properties of sodium alginate and chitosan composite films through sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP) crosslinking. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;264(Pt 2):130463. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.130463; PMID: 38423442
34. Oryan A, Mohammadalipour A, Moshiri A, Tabandeh MR. Topical application of aloe vera accelerated wound healing, modeling, and remodeling. Ann Plast Surg. 2016;77(1):37–46. DOI: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000239; PMID: 25003428
35. Loo HL, Goh BH, Lee LH, Chuah LH. Application of chitosan-based nanoparticles in skin wound healing. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022;17(3):299-332. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajps.2022.04.001
36. Hajialyani M, Tewari D, Sobarzo-Sánchez E, Nabavi SM, Farzaei MH, Abdollahi M. Natural product-based nanomedicines for wound healing purposes: therapeutic targets and drug delivery systems. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018;13:5023-43. DOI: 10.2147/ijn.s174072; PMCID: PMC6128268; PMID: 30214204
37. Thakur R, Jain N, Pathak R, Sandhu SS. Practices in wound healing studies of plants. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:2011:438056. DOI: 10.1155/2011/438056; PMCID: PMC3118986; PMID: 21716711
38. Schilrreff P, Alexiev U. Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Skin Wounds and Promising Natural Bioactive Compounds Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(9):4928. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094928; PMCID: PMC9104327; PMID: 35563319
39. Deka B, Bhattacharjee B, Shakya A, Ikbal AMA, Goswami C, Sarma S. Mechanism of Action of Wound Healing Activity of Calendula officinalis: A Comprehensive Review. Pharm Biosci J. 2021;9(1):28-44. DOI: 10.20510/ukjpb/9/i1/1609684673
40. Razika L, Thanina AC, Nadjiba CM, Narimen B, Mahdi DM, Karim A. Antioxidant and wound healing potential of saponins extracted from the leaves of Algerian Urtica dioica L. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2017;30(3(Suppl.)):1023-9. PMID: 28655702
41. Ambreen M, Mirza SA. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory and wound healing potential of tannins isolated from leaf callus cultures of Achyranthes aspera and Ocimum basilicum. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2020;33(1(Supplementary)):361-9. PMID: 32122869
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Fathnur Sani Kasmadi, Ave Olivia Rahman, Havizur Rahman, Yuliawati Yuliawati, Agung Giri Samudra

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.