Post-COVID Mucormycosis: An Emerging Threat in Developing Countries - A Prospective Review
Abstract
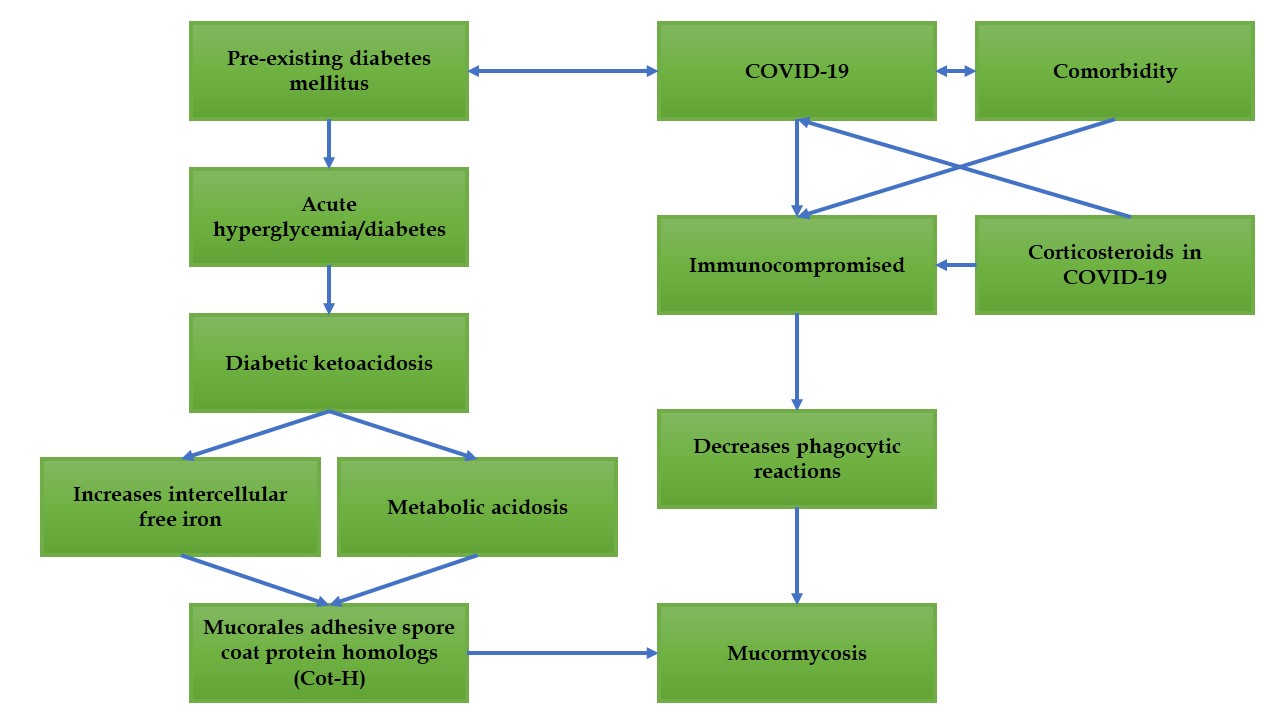
COVID-19, with its rapidly mutating strains, poses a significant global health challenge. Recent reports of a surge in mucormycosis cases among COVID-19 patients highlight the urgent need for understanding and addressing this critical complication. This review explores the factors contributing to mucormycosis development in COVID-19 patients and outlines strategies for prevention and management. Several factors, including high glucose levels (diabetes, onset, steroid-induced hyperglycemia), low oxygen levels, elevated iron levels (especially ferritin), metabolic acidosis, and diabetic ketoacidosis, can facilitate the germination of mucor spores. COVID-19 patients with underlying conditions such as diabetes, cancer, or organ transplants are particularly susceptible to mucormycosis due to their immunocompromised state. The growth of the mucor pathogen requires free iron, which is elevated in conditions like diabetic ketoacidosis. This elevated iron level promotes the formation of Cot-H, a crucial component of fungal growth, leading to mucormycosis. Additionally, comorbidities and corticosteroids can suppress the immune system, hindering the body's ability to fight off infections like mucormycosis. Therefore, it is imperative to avoid the indiscriminate use of corticosteroids. Strict control of acute hyperglycemia and comprehensive monitoring of diabetic and immunocompromised COVID-19 patients are essential preventive measures. By addressing these factors, healthcare providers can mitigate the risk of mucormycosis in COVID-19 patients and improve overall outcomes.
Full text article
References
2. Cucinotta D, Vanelli M. WHO Declares COVID-19 a Pandemic.Acta Biomed. 2020;91(1):157-60. DOI: 10.23750/abm.v91i1.9397; PMCID: PMC7569573; PMID: 32191675
3. Chakraborty D, Yolmo NL. Fright of Covid-19 and its Future: A Review. J Palliat Care Med. 2020;10(4):1000369. DOI: 10.4172/2165-7386.1000369
4. Paltauf A. Mycosis mucorina. Archiv F Pathol Anat. 1885;102:543-64. DOI: 10.1007/BF01932420
5. Baker RD. Mucormycosis-a new disease? J Am Med Assoc. 1957; 163(10):805-8. DOI: 10.1001/jama.1957.02970450007003; PMID: 13405736
6. Mahalaxmi I, Jayaramayya K, Venkatesan D, Subramaniam MD, Renu K, Vijayakumar P, et al. Mucormycosis: An opportunistic pathogen during COVID-19. Environ Res. 2021;201:111643. DOI: 10.1016/j.envres.2021.111643; PMCID: PMC8258024; PMID: 34237335
7. Singh R, Mittal G, kakati B, Koul N. An Observational Study of Fungal Infections in COVID-19: Highlighting the Role of Mucormycosis in Tertiary Healthcare Settings. Cureus. 2024;16(3):e57295. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.57295; PMCID: PMC11059081; PMID: 38690487
8. Chillana S, Chilana KAM. COVID-19 and Mucormycosis: A Black Fungus Disaster? Indian J Dermatol. 2022;67(5):535-8. DOI: 10.4103/ijd.ijd_17_22; PMCID: PMC9971779; PMID: 36865825
9. Pollard CA, Morran MP, Nestor-Kalinoski AL. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a global health crisis, with millions of deaths reported to the WHO. Physiol Genomics. 2020;52(11):549-57. DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00089.2020; PMCID: PMC7686876; PMID: 32991251
10. Skiada A, Pavleas I, Drogari-Apiranthitou M. Epidemiology and diagnosis of mucormycosis: An Update. J Fungi. 2020;6(4):265. DOI: 10.3390/jof6040265; PMCID: PMC7711598; PMID: 33147877
11. Chander J, Kaur M, Singla N, Punia RPS, Singhal SK, Attri AK, et al. Mucormycosis: Battle with the Deadly Enemy over a Five-Year Period in India. J Fungi. 2018;4(2):46. DOI: 10.3390/jof4020046; PMCID: PMC6023269; PMID: 29642408
12. Prakash H, Chakrabarti A. Global Epidemiology of Mucormycosis. J Fungi. 2019;5(1):26. DOI: 10.3390/jof5010026; PMCID: PMC6462913; PMID: 30901907
13. Jeong W, Keighley C, Wolfe R, Lee WL, Slavin MA, Kongn DCM, et al. The epidemiology and clinical manifestations of mucormycosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of case reports. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019;25(1):26–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.07.011; PMID: 30036666
14. Singh AK, Singh R, Joshi SR, Misra A. Mucormycosis in COVID-19: A systematic review of cases reported worldwide and in India. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2021;15(4):102146. DOI: 10.1016/j.dsx.2021.05.019; PMCID: PMC8137376; PMID: 34192610
15. Faria L, Mahin T, Qader MA, Ahmed M, Anwar MA. A Case of Post-COVID-19 Rhino-Cerebral Mucormycosis in an Immunocompromised Patient. Cureus. 2023;15(7):e42652. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.42652; PMCID: PMC10461695; PMID: 37644947
16. Mehta S, Pandey A. Rhino-Orbital Mucormycosis Associated With COVID-19. Cureus 2020;12(9):e10726. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.10726; PMCID: PMC7599039; PMID: 33145132
17. Bayram N, Ozsaygılı C, Sav H, Tekin Y, Gundogan M, Pangal E, et al., Susceptibility of severe COVID-19 patients to rhino-orbital mucormycosis fungal infection in different clinical manifestations. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2021;65(4):515-25. DOI: 10.1007/s10384-021-00845-5; PMCID: PMC8165350; PMID: 34057620
18. Moorthy A, Gaikwad R, Krishna S, Hegde R, Tripathi KK, Kale PG, et al. SARS-CoV-2, Uncontrolled Diabetes and Corticosteroids—An Unholy Trinity in Invasive Fungal Infections of the Maxillofacial Region? A Retrospective, Multi-centric Analysis. J Maxillofac Oral Surg. 2021;20(3):418-25. DOI: 10.1007/s12663-021-01532-1; PMCID: PMC7936599; PMID: 33716414
19. Veisi A, Bagheri A, Eshaghi M, Rikhtehgar MH, Kanavi MR, Farjad R. Rhino-orbital mucormycosis during steroid therapy in COVID-19 patients: A case report. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2022;32(4):NP11-6. DOI: 10.1177/11206721211009450; PMCID: PMC9294610; PMID: 33843287
20. Satish D, Joy D, Ross A, Balasubramanya. Mucormycosis coinfection associated with global COVID-19: acase series from India. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021;7(5):815-20. DOI: 10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20211574
21. Revannavar SM, Supriya PS, Samaga L, Vineeth VK. COVID-19 triggering mucormycosis in a susceptible patient: a new phenomenon in the developing world? BMJ Case Rep. 2021;14(4):e241663. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2021-241663; PMCID: PMC8088249; PMID: 33906877
22. Hassan FA, Aljahli M, Molani F, Almomen A. Rhino-orbito-cerebral mucormycosis in patients with uncontrolled diabetes: A case series. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;73:324–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.07.011; PMCID: PMC7393455; PMID: 32738774
23. Pandilwar PK, Khan K, Shah K, Sanap M, Unnikrishnan KSA, Nerurkar S. Mucormycosis: A rare entity with rising clinical presentation inimmunocompromised hosts. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;77:57–61. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.10.075; PMCID: PMC7644794; PMID: 33152595
24. El-Shabasy RM, Nayel MA, Taher MM, Abdelmonem R, Shoueir KR, Kenawy ER. Three waves changes, new variant strains, and vaccination effect against COVID-19 pandemic. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022;204:161-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.01.118; PMCID: PMC8782737; PMID: 35074332
25. Thakur V, Bhola S, Thakur P, Patel SKS, Kulshrestha S, Ratho RK, et al. Waves and variants of SARS-CoV-2: understanding the causes and effect of the COVID-19 catastrophe. Infection. 2022;50(2):309-25. DOI: 10.1007/s15010-021-01734-2; PMCID: PMC8675301; PMID: 34914036
26. Moore S, Hill EM, Tildesley MJ, Dyson L, Keeling MJ. Vaccination and non-pharmaceutical interventions for COVID-19: a mathematical modelling study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2021;21(6):793-802. DOI: 10.1016/s1473-3099(21)00143-2; PMCID: PMC7972312; PMID: 33743847
27. Islam MA. A review of SARS-CoV-2 variants and vaccines: Viral properties, mutations, vaccine efficacy, and safety. Infect Med. 2023;2(4):247-61. DOI: 10.1016/j.imj.2023.08.005; PMCID: PMC10774670; PMID: 38205179
28. Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, Ali S, Gao H, Bhore R, et al. REGN-COV2, a Neutralizing Antibody Cocktail, in Outpatients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(3):238-51. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035002; PMCID: PMC7781102; PMID: 33332778
29. Baum A, Fulton BO, Wloga E, Copin R, Pascal KE, Russo V, et al. Antibody cocktail to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies. Science 2020;369(6506):1014–8. DOI: 10.1126/science.abd0831; PMCID: PMC7299283; PMID: 32540904
30. Hoenigl M, Seidel D, Carvalho A, Rudramurthy SM, Arastehfar A, Gangneuz JP, et al. The emergence of COVID-19 associated mucormycosis: a review of cases from 18 countries. Lancet Microbe. 2022;3(7):e543-52. DOI: 10.1016/s2666-5247(21)00237-8; PMCID: PMC8789240; PMID: 35098179
31. Sharma A, Goel A. Mucormycosis: risk factors, diagnosis, treatments, and challenges during COVID-19 pandemic. Folia Microbiol. 2022;67(3):363-87. DOI: 10.1007/s12223-021-00934-5; PMCID: PMC8881997; PMID: 35220559
32. Parfrey NA. Improved diagnosis and prognosis of mucormycosis. A clinicopathologic study of 33 cases. Medicine. 1986;65(2):113-23. DOI: 10.1097/00005792-198603000-00004; PMID: 3951358
33. Howard DH. Iron gathering by zoopathogenic fungi. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2004;40(2):95-100. DOI: 10.1016/S0928-8244(03)00301-8; PMID: 15040387
34. Howard DH. Acquisition, transport, and storage of iron by pathogenic fungi. Clin Microbiol Rev 1999;12(3):394–404. DOI: 10.1128/cmr.12.3.394; PMCID: PMC100245; PMID: 10398672
35. Gebremariam T, Lin L, Liu M, Kontoyiannis DP, French S, Edwards Jr JE, et al., Bicarbonate correction of ketoacidosis alters host-pathogen interactions and alleviates mucormycosis. J Clin Invest. 2016;126(6):2280-94. DOI: 10.1172/jci82744; PMCID: PMC4887168; PMID: 27159390
36. Ibrahim AS, Spellberg B, Walsh TJ, Kontoyiannis DP. Pathogenesis of Mucormycosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(Suppl 1):S16–22. DOI: 10.1093/cid/cir865; PMCID: PMC3286196; PMID: 22247441
37. Hassan MIA, Voigt K. Pathogenicity patterns of mucormycosis: epidemiology, interaction with immune cells and virulence factors. Med Mycol. 2019;57(Suppl 2):S245–56. DOI: 10.1093/mmy/myz011; PMCID: PMC6394756; PMID: 30816980
38. Mirza M, Verma M, Sahoo SS, Roy S, Kakkar R, Singh DK. India's Multi-Sectoral Response to Oxygen Surge Demand during COVID-19 Pandemic: A Scoping Review. Indian J Community Med. 2023;48(1):31-40. DOI: 10.4103/ijcm.ijcm_665_22; PMCID: PMC10112770; PMID: 37082381
39. Alshahawey MG, El-Housseiny GS, Elsayed NS, Alshahrani MY, Wakeel LM, Aboshanab KM. New insights on mucormycosis and its association with the COVID-19 pandemic. Future Sci OA. 2021;8(2):FSO772. DOI: 10.2144/fsoa-2021-0122; PMCID: PMC8686842; PMID: 35059222
40. Spellberg B, Walsh TJ, Kontoyiannis DP, Edwards Jr J, Ibrahim AS. Recent advances in the management of mucormycosis: from bench to bedside. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(12):1743-51. DOI: 10.1086/599105; PMCID: PMC2809216; PMID: 19435437
41. Smith C, Lee SC. Current treatments against mucormycosis and future directions. PLoS Pathog. 2022;18(10):e1010858. DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010858; PMCID: PMC9560507; PMID: 36227854
42. Dwivedi AK. Black Fungus/Mucormycosis and Homeopathic Treatment. Int J Sci Res. 2021:10(8):71-2. DOI: 10.36106/ijsr
43. Wolthers MS, Schmidt G, Gjørup CA, Helweg-Larsen J, Rubek N, Jensen LT. Surgical management of rhinocerebral mucormycosis: A case series. JPRAS Open. 2021;30:33-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2021.04.013; PMCID: PMC8358096; PMID: 34401438
Authors
Copyright (c) 2024 Debpratim Chakraborty, Sudipa Adhikary

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.