Computational Drug Design against Ebola Virus Targeting Viral Matrix Protein VP30
Abstract
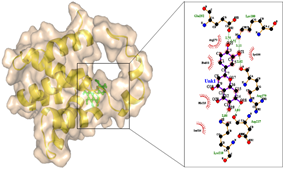
Ebola viral disease (EVD) is a deadly infectious hemorrhagic viral fever caused by the Ebola virus with a high mortality rate. Until date, there is no effective drug or vaccination available to combat this condition. This study focuses on designing an effective antiviral drug for Ebola viral disease targeting viral protein 30 (VP30) of Ebola virus, highly required for transcription initiation. The lead molecules were screened for Lipinski rule of five, ADMET study following which molecular docking and bioactivity prediction was carried out. The compounds with the least binding energy were analyzed using interaction software. The results revealed that 6-Hydroxyluteolin and (-)-Arctigenin represent active lead compounds that inhibit the activity of VP30 protein and exhibits efficient pharmacokinetics. Both these compounds are plant-derived flavonoids and possess no known adverse effects on human health. In addition, they bind strongly to the predicted binding site centered on Lys180, suggesting that these two lead molecules can be imperative in designing a potential drug for EVD.
Full text article
References
Aminpour, M., Montemagno, C., Tuszynski, J.A. 2019. An Overview of Molecular Modeling for Drug Discovery with Specific Illustrative Examples of Applications. Molecules. 24(9):1693. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules24091693
Ascenzi, P., Bocedi, A., Heptonstall, J., Capobianchi, M.R., Di Caro, A., Mastrangelo, E., Bolognesi, M., Ippolito, G. 2008. Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus: insight the Filoviridae family. Molecular Aspects of Medicine. 29(3):151-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2007.09.005
Baikerikar, S. 2017. Curcumin and Natural Derivatives Inhibit Ebola Viral Proteins: An In Silico Approach. Pharmacognosy Research. 9(Suppl 1):S15-S22. https://dx.doi.org/10.4103/pr.pr_30_17
Baize, S., Pannetier, D., Oestereich, L., Rieger, T., Koivogui, L., Magassouba, N., Soropogui, B., Sow, M.S., Keita, S., de Clerck, H., Tiffany, A., Dominguez, G., Loua, M., Traore, A., Kolie, M., Malano, E.R., Heleze, E., Bocquin, A., Mely, S., Raoul, H. Caro, V., Cadar, D., Gabriel, M., Pahlmann, M., Tappe, D., Schmidt-Chanasit, J., Impouma, B., Diallo, A.K., Formenty, P., Herp, M.V., Gunther, S. 2014. Emergence of Zaire Ebola Virus Disease in Guinea. New England Journal of Medicine. 371(15):1418-1425. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1404505
Basler, C.F. 2015. Innate Immune Evasion by Filoviruses. Virology. 479-480:122-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.030
Berman, H.M., Westbrook, J., Feng, Z., Gilliland, G., Bhat, T.N., Weissig, H., Shindyalov, I.N., Bourne, P.E. 2000. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Research. 28(1):235-242. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.235
Biedenkopf, N., Hartlieb, B., Hoenen, T., Becker, S. 2013. Phosphorylation of Ebola Virus VP30 Influences the Composition of the Viral Nucleocapsid Complex: Impact on Viral Transcription and Replication. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288(16):11165-11174. https://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.461285
Binkowski, T.A., Naghibzadeh, S., Liang, J. 2003. CASTp: Computed Atlas of Surface Topography of proteins. Nucleic Acids Research. 31(13):3352-3355. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg512
Broadhurst, M.J., Brooks, T.J.G., Pollock, N.R. 2016. Diagnosis of Ebola Virus Disease: Past, Present, and Future. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 29(4):773-793. https://dx.doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00003-16
Cantoni, D., Rossman, J.S. 2018. Ebolaviruses: New roles for old proteins. PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. 12(5):e0006349. https://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0006349
Chiappelli, F., Bakhordarian, A., Thames, A.D., Du, A.M., Jan, A.L., Nahcivan, M., Nguyen, M.T., Sama, N., Manfrini, E., Piva, F., Rocha, R.M., Maida, C.A. 2015. Ebola: translational science considerations. Journal of Translational Medicine. 13:11. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12967-014-0362-3
De Clercq, E. 2015. Ebola virus (EBOV) infection: Therapeutic strategies. Biochemical Pharmacology. 93(1):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2014.11.008
de La Vega, M.A., Wong, G., Kobinger, G.P., Qiu, X. 2015. The multiple roles of sGP in Ebola pathogenesis. Viral Immunology. 28(1):3-9. https://doi.org/10.1089/vim.2014.0068
de Ruyck, J., Brysbaert, G., Blossey, R., Lensink, M.F. 2016. Molecular docking as a popular tool in drug design, an in silico travel. Advances and Applications in Bioinformatics and Chemistry. 9:1-11. https://dx.doi.org/10.2147/AABC.S105289
Dhama, K., Karthik, K., Khandia, R., Chakraborty, S., Munjal, A., Latheef, S.K., Kumar, D., Ramakrishnan, M.A., Malik, Y.S., Singh, R., Malik, S.V.S., Singh, R.K., Chaicumpa, W. 2018. Advances in Designing and Developing Vaccines, Drugs, and Therapies to Counter Ebola Virus. Frontiers in Immunology. 9:1803. https://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01803
Easton, V., McPhillie, M., Garcia-Dorival, I., Barr, J.N., Edwards, T.A., Foster, R., Fishwick, C., Harris, M. 2018. Identification of a small molecule inhibitor of Ebola virus genome replication and transcription using in silico screening. Antiviral Research. 156:46-54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.antiviral.2018.06.003
Feldmann, H., Geisbert, T.W. 2011. Ebola haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 377(9768):849-862. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60667-8
Forli, S., Huey, R., Pique, M.E., Sanner, M., Goodsell, D.S., Olson, A.J. 2016. Computational protein-ligand docking and virtual drug screening with the AutoDock suite. Nature Protocols. 11(5):905-919. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2016.051
Garcia-Godoy, M.J., Lopez-Camacho, E., Garcia-Nieto, J., Nebro, A.J., Aldana-Montes, J.F. 2015. Solving Molecular Docking Problems with Multi-Objective Metaheuristics. Molecules. 20(6):10154-10183. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/molecules200610154
Geisbert, T.W., Jahrling, P.B. 1995. Differentiation of filoviruses by electron microscopy. Virus Research. 39(2-3):129-150. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1702(95)00080-1
Gore, S., Garcia, E.S., Hendrickx, P.M.S., Gutmanas, A., Westbrook, J.D., Yang, H., Feng, Z., Baskaran, K., Berrisford, J.M., Hudson, B.P., Ikegawa, Y., Kobayashi, N., Lawson, C.L., Mading, S., Mak, L., Mukhopadhyay, A., Oldfield, T.J., Patwardhan, A., Peisach, E., Sahni, G., Sekharan, M.R., Sen, S., Shao, C., Smart, O.S., Ulrich, E.L., Yamashita, R., Quesada, M., Young, J.Y., Nakamura, H., Markley, J.L., Berman, H.M., Burley, S.K., Velankar, S., Kleywegt, G.J. 2017. Validation of Structures in the Protein Data Bank. Structure. 25(12):1916-1927. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2017.10.009
Guex, N., Peitsch, M.C. 1997. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis. 18(15):2714-2723. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150181505
Hartlieb, B., Muziol, T., Weissenhorn, W., Becker, S. 2007. Crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of Ebola virus VP30 reveals a role in transcription and nucleocapsid association. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104(2):624-629. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0606730104
Hoenen, T., Volchkov, V., Kolesnikova, L., Mittler, E., Timmins, J., Ottmann, M., Reynard, O., Becker, S., Weissenhorn, W. 2005. VP40 octamers are essential for Ebola virus replication. Journal of Virology. 79(3):1898-1905. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.79.3.1898-1905.2005
Huggins, J., Zhang Z.X., Bray, M. 1999. Antiviral drug therapy of filovirus infections: S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitors inhibit Ebola virus in vitro and in a lethal mouse model. The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 179(Suppl 1):S240-S247. https://doi.org/10.1086/514316
Joshi, A., Kumar, R., Sharma, A. 2018. Molecular Docking Studies, Bioactivity Score Prediction, Drug Likeness Analysis of GSK-3 Β Inhibitors: A Target Protein Involved in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosciences Biotechnology Research Asia. 15(2):455-467. http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/bbra/2650
Khan, T., Dixit, S., Ahmad, R., Raza, S., Azad, I., Joshi, S., Khan, A.R. 2017. Molecular docking, PASS analysis, bioactivity score prediction, synthesis, characterization and biological activity evaluation of a functionalized 2-butanone thiosemicarbazone ligand and its complexes. Journal of Chemical Biology. 10(3):91-104. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12154-017-0167-y
Kim, S., Thiessen, P.A., Bolton, E.E., Chen, J., Fu, G., Gindulyte, A., Han, L., He, J., He, S., Shoemaker, B.A., Wang, J., Yu, B., Zhang, J., Bryant, S.H. 2016. PubChem Substance and Compound databases. Nucleic Acids Research. 44(D1):D1202-1213. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv951
Kouznetsova, J., Sun, W., Martinez-Romero, C., Tawa, G., Shinn, P., Chen, C.Z., Schimmer, A., Sanderson, P., McKew, J.C., Zheng, W., Garcia-Sastre, A. 2014. Identification of 53 compounds that block Ebola virus-like particle entry via a repurposing screen of approved drugs. Emerging Microbes & Infections. 3(12):e84. https://doi.org/10.1038/emi.2014.88
Laskowski, R.A., Swindells, M.B. 2011. LigPlot+: multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 51(10):2778-2786. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci200227u
Lee, J.E., Saphire, E.O. 2009. Ebolavirus glycoprotein structure and mechanism of entry. Future Virology. 4(6):621-635. https://doi.org/10.2217/fvl.09.56
Lipinski, C.A. 2004. Lead- and drug-like compounds: the rule-of-five revolution. Drug Discovery Today: Technologies. 1(4):337-341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddtec.2004.11.007
Martinez, M.J., Biedenkopf, N., Volchkova, V., Hartlieb, B., Alazard-Dany, N., Reynard, O., Becker, S., Volchkov, V. 2008. Role of Ebola Virus VP30 in Transcription Reinitiation. Journal of Virology. 82(24):12569-12573. https://dx.doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01395-08
Mühlberger, E. 2007. Filovirus replication and transcription. Future Virology. 2(2):205-215. https://dx.doi.org/10.2217/17460794.2.2.205
Nasution, M.A.F., Toepak, E.P., Alkaff, A.H., Tambunan, U.S.F. 2018. Flexible docking-based molecular dynamics simulation of natural product compounds and Ebola virus Nucleocapsid (EBOV NP): a computational approach to discover new drug for combating Ebola. BMC Bioinformatics. 19(Suppl 14):419. https://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2387-8
Passi, D., Sharma, S., Dutta, S.R., Dudeja, P., Sharma, V. 2015. Ebola Virus Disease (The Killer Virus): Another Threat to Humans and Bioterrorism: Brief Review and Recent Updates. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research. 9(6):LE01-LE08. https://dx.doi.org/10.7860/JCDR/2015/13062.6100
Picazo, E., Jahrling, P.B. 2015. Small molecule inhibitors of ebola virus infection. Drug Discovery Today. 20(2):277-286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drudis.2014.12.010
Pires, D.E., Blundell, T.L., Ascher, D.B. 2015. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 58(9):4066-4072. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00104
Raj, U., Varadwaj, P.K. 2016. Flavonoids as Multi-Target Inhibitors for Proteins Associated with Ebola Virus: In Silico Discovery Using Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Studies. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences. 8(2):132-141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12539-015-0109-8
Roca, A., Afolabi, M.O., Saidu, Y., Kampmann, B. 2015. Ebola: A holistic approach is required to achieve effective management and control. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. 135(4):856-867. https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.02.015
Sadowski, J., Gasteiger, J., Klebe, G. 1994. Comparison of Automatic Three-Dimensional Model Builders Using 639 X-ray Structures. Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences. 34(4):1000-1008. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci00020a039
Salata, C., Calistri, A., Alvisi, G., Celestino, M., Parolin, C., Palu, G. 2019. Ebola Virus Entry: From Molecular Characterization to Drug Discovery. Viruses. 11(3):274. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v11030274
Saleh, N.A., Elshemey, W.M. 2017. Structure-based drug design of novel peptidomimetic cellulose derivatives as HCV-NS3 protease inhibitors. Life Sciences. 187:58-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.08.021
Schuler, J., Hudson, M.L., Schwartz, D., Samudrala, R. 2017. A Systematic Review of Computational Drug Discovery, Development, and Repurposing for Ebola Virus Disease Treatment. Molecules. 22(10):E1777. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22101777
Seeliger, D., de Groot, B.L. 2010. Ligand docking and binding site analysis with PyMOL and Autodock/Vina. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 24(5):417-422. https://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10822-010-9352-6
Shen, Z., Lou, K., Wang, W. 2015. New small-molecule drug design strategies for fighting resistant influenza A. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 5(5):419-430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2015.07.006
Sneha, P., Doss, C.G.P. 2016. Gliptins in managing diabetes - Reviewing computational strategy. Life Sciences. 166:108-120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.10.009
Venkatesan, A., Febin, P.D.J. 2017. Deciphering molecular properties and docking studies of hepatitis C and non-hepatitis C antiviral inhibitors - A computational approach. Life Sciences. 174:8-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.02.014
Venkatesan, A., Rambabu, M., Jayanthi, S., Febin, P.D.J. 2018. Pharmacophore feature prediction and molecular docking approach to identify novel anti-HCV protease inhibitors. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 119(1):960-966. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26262
Vlietinck, A.J., De Bruyne, T., Apers, S., Pieters, L.A. 1998. Plant-derived leading compounds for chemotherapy of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Planta Medica. 64(2):97-109. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-957384
Warren, T.K., Wells, J., Panchal, R.G., Stuthman, K.S., Garza, N.L., Van Tongeren, S.A., Dong, L., Retterer, C.J., Eaton, B.P., Pegoraro, G., Honnold, S., Bantia, S., Kotian, P., Chen, X., Taubenheim, B.R., Weich, L.S., Minning, D.M., Babu, Y.S., Sheridan, W.P., Bavari, S. 2014. Protection against filovirus diseases by a novel broad-spectrum nucleoside analogue BCX4430. Nature. 508(7496):402-405. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13027
Weik, M., Modrof, J., Klenk, H.D., Becker, S., Mühlberger, E. 2002. Ebola virus VP30-mediated transcription is regulated by RNA secondary structure formation. Journal of Virology. 76(17):8532-8539. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.76.17.8532-8539.2002
Xie, H., Li, Y., Yu, F., Xie, X., Qiu, K., Fu, J. 2015. An Investigation of Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamic Simulation on Imidazopyridines as B-Raf Kinase Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 16(11):27350-27361. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms161126026
Xu, W., Luthra, P., Wu, C., Batra, J., Leung, D.W., Basler, C.F., Amarasinghe, G.K. 2017. Ebola virus VP30 and nucleoprotein interactions modulate viral RNA synthesis. Nature Communications. 8:15576. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15576
Yannai, S. 2003. Dictionary of Food Compounds with CD-ROM: Additives, Flavors, and Ingredients. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420068450
Yu, D.S., Weng, T.H., Wu, X.X., Wang, F.X.C., Lu, X.Y., Wu, H.B., Wu, N.P., Li, L.J., Yao, H.P. 2017. The lifecycle of the Ebola virus in host cells. Oncotarget. 8(33):55750-55759. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18498
Zhao, Y. 2016. Towards Structural Based Drug Development for Ebola Virus Disease. Journal of Chemical Biology & Therapeutics. 1(1):e102. https://doi.org/10.4172/2572-0406.1000e101
Authors
Copyright (c) 2019 Arthi Venkatesan, Lavanya Ravichandran, J Febin Prabhu Dass

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.