Regulatory Reform and Policy Mapping in Indonesia’s Traditional Medicine, Health Supplement, and Cosmetic Sectors
Abstract
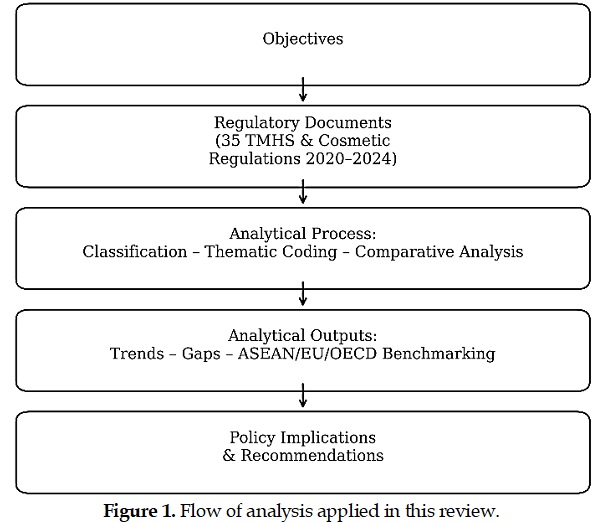
This study systematically analyzed Indonesia's regulatory reforms for traditional medicines, health supplements, and cosmetics (TMHSC) issued between 2020 and 2024. The objective was to map the scope, distribution, and policy orientation of the 35 regulations enacted by the Indonesian Food and Drug Authority (BPOM) within the framework of the National Medium-Term Development Plan (RPJMN 2020–2024). A qualitative policy analysis was employed, combining document analysis, thematic coding, and comparative benchmarking with frameworks from the ASEAN, European Union (EU), and Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). The findings show that 25 regulations were directed toward strengthening regulatory services, nine targeted compliance and Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), and one supported research and innovation through preclinical testing standards. This distribution reflects a policy trajectory that prioritizes service delivery and compliance assurance, while progressively integrating evidence-based approaches to research and innovation. A comparative analysis revealed a strong alignment with ASEAN harmonization initiatives and an incremental adoption of international benchmarks, such as ISO 22716 for cosmetics and the WHO GMP guidelines for herbal medicines. Overall, Indonesia's TMHSC regulatory transformation demonstrates a balanced and adaptive governance model that safeguards public health, promotes innovation, and enhances regional policy coherence. The results provide practical implications for policymakers, particularly BPOM and ASEAN member states, in developing regulatory frameworks that effectively balance consumer protection, innovation enablement, and market competitiveness within the TMHSC sectors.
Full text article
References
2. Grazina L, Mafra I, Monaci L, Amaral JS. Mass spectrometry-based approaches to assess the botanical authenticity of dietary supplements. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2023;22(5):3870-909. DOI: 10.1111/1541-4337.13222; PMID: 37548598
3. Lindberg K, Martvall A, Lima MGB, Franca CSS. Herbal medicine promotion for a restorative bioeconomy in tropical forests: A reality check on the Brazilian Amazon. For Policy Econ. 2023;155:103058. DOI: 10.1016/j.forpol.2023.103058
4. Wang H, Chen Y, Wang L, Liu Q, Yang S, Wang C. Advancing herbal medicine: enhancing product quality and safety through robust quality control practices. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1265178. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265178; PMCID: PMC10561302; PMID: 37818188
5. Liu C, Sun CK, Chang YC, Yang SY, Liu T, Yang CC. The Impact of the Fear of COVID-19 on Purchase Behavior of Dietary Supplements: Integration of the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Protection Motivation Theory. Sustainability. 2021;13(22):12900. DOI: 10.3390/su132212900
6. Budiyoko B, Zulkifli L, Dharmawan B, Sunendar S, Rachmah MA, Prasetyo K, et al. Unlocking the sustainable livelihoods strategy for forest communities in the southern slope of Mount Slamet, Indonesia. Sustain Debate. 2024;15(1):216–32. DOI: 10.18472/SustDeb.v15n1.2024.52568
7. Cahyaningsih R, Brehm JM, Maxted N. Setting the priority medicinal plants for conservation in Indonesia. Genet Resour Crop Evol. 2021;68(5):2019–50. DOI: 10.1007/s10722-021-01115-6
8. Wirabuana PYAP, Baskorowati L, Pamungkas B, Mulyana B, South J, Purnobasuki H, et al. Mangroves, fauna compositions and carbon sequestration after ten years restoration on Flores Island, Indonesia. Sci Rep. 2025;15(1):4866. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-87307-x
9. Ahn S, Zhou J, Jiang D, Kerr S, Zhu Y, Song P, et al. WHO global research priorities for traditional, complementary, and integrative (TCI) medicine: an international consensus and comparisons with LLMs. J Glob Health. 2025;15:04336. DOI: 10.7189/jogh.15.04336; PMCID: PMC12615007; PMID: 41232122.
10. Gafner S, Blumenthal M, Foster S, Cardellina JH 2nd, Khan IA, Upton R. Botanical Ingredient Forensics: Detection of Attempts to Deceive Commonly Used Analytical Methods for Authenticating Herbal Dietary and Food Ingredients and Supplements. J Nat Prod. 2023;86(2):460-72. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.2c00929; PMCID: PMC9972475; PMID: 36716213
11. Ichim MC, de Boer HJ. A Review of Authenticity and Authentication of Commercial Ginseng Herbal Medicines and Food Supplements. Front Pharmacol. 2021;11:612071. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.612071; PMCID: PMC7832030; PMID: 33505315
12. Kozhuharov VR, Ivanov K, Karcheva-Bahchevanska D, Prissadova N, Ivanova S. Development and Validation of Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method for Quantification of Sibutramine in Dietary Supplements. Processes. 2023;11(8):2337. DOI: 10.3390/pr11082337
13. Wierzejska RE. Dietary Supplements—For Whom? The Current State of Knowledge about the Health Effects of Selected Supplement Use. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(17):8897. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18178897; PMCID: PMC8431076; PMID: 34501487
14. Gupta V, Mohapatra S, Mishra H, Farooq U, Kumar K, Ansari M, et al. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals—A Review of Latest Advancements. Gels. 2022;8(3):173. DOI: 10.3390/gels8030173; PMCID: PMC8951203; PMID: 35323286
15. Sharma A, Agarwal P, Sebghatollahi Z, Mahato N. Functional Nanostructured Materials in the Cosmetics Industry: A Review. ChemEngineering. 2023;7(4):66. DOI: 10.3390/chemengineering7040066
16. Kumar V, Kumar N, Singh G. Natural Products and Derivatives Applied for Skin Care: An Updated Review. Curr Tradit Med. 2024;10(1):e180123212858. DOI: 10.2174/2215083809666230118141457
17. Lähteenmäki-Uutela A, Rahikainen M, Camarena-Gómez MT, Piiparinen J, Spilling K, Yang B. European Union legislation on macroalgae products. Aquac Int. 2021;29(2):487–509. DOI: 10.1007/s10499-020-00633-x
18. Necoechea-Porras PD, López A, Salazar-Elena JC. Deregulation in the Energy Sector and Its Economic Effects on the Power Sector: A Literature Review. Sustainability. 2021;13(6):3429. DOI: 10.3390/su13063429
19. Zhang L, Pham TD, Li R, Do TT. Enhancing the Sustainable Development of the ASEAN’s Digital Trade: The Impact Mechanism of Innovation Capability. Sustainability. 2025;17(4):1766. DOI: 10.3390/su17041766
20. Göttems LBD, Mollo MDLR. Neoliberalism in Latin America: effects on health system reforms. Rev Saúde Pública. 2020;54:74. DOI: 10.11606/s1518-8787.2020054001806; PMCID: PMC7371409; PMID: 32725099
21. Hajighasemi A, Oghazi P, Aliyari S, Pashkevich N. The impact of welfare state systems on innovation performance and competitiveness: European country clusters. J Innov Knowl. 2022;7(4):100236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jik.2022.100236
22. Raudla R, Mohr Z, Douglas JW. Which managerial reforms facilitate public sector innovation? Public Adm. 2024;102(2):771–88. DOI: 10.1111/padm.12951
23. Brendler T, Brinckmann JA, Feiter U, Gericke N, Lang L, Pozharitskaya ON, et al. Sceletium for Managing Anxiety, Depression and Cognitive Impairment: A Traditional Herbal Medicine in Modern-Day Regulatory Systems. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2021;19(9):1384-400. DOI: 10.2174/1570159X19666210215124737; PMCID: PMC8762184; PMID: 33588735
24. Yi S, Yam ELY, Cheruvettolil K, Linos E, Gupta A, Palaniappan L, et al. Perspectives of Digital Health Innovations in Low- and Middle-Income Health Care Systems from South and Southeast Asia. J Med Internet Res. 2024;26:e57612. DOI: 10.2196/57612; PMCID: PMC11629033; PMID: 39586089
25. Phan TC. Impact of green investments, green economic growth and renewable energy consumption on environmental, social, and governance practices to achieve the sustainable development goals: A sectoral analysis in the ASEAN economies. Int J Eng Bus Manag. 2024;16:18479790241231725
26. Mponda JS, Muula AS, Choko A, Ajuwon AJ, Moody JO. Traditional medicine regulation status and challenges in Malawi and Nigeria. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025;25(1):53. DOI: 10.1186/s12906-025-04812-2; PMCID: PMC11829355; PMID: 39953523
27. Icasiano CDA, Taeihagh A. Governance of the Risks of Ridesharing in Southeast Asia: An In-Depth Analysis. Sustainability. 2021;7;13(11):6474. DOI: 10.3390/su13116474
28. Bowen GA. Document Analysis as a Qualitative Research Method. Qual Res J. 2009;9(2):27–40. DOI: 10.3316/QRJ0902027
29. Ghimire N, Basnet R, Acharya R, Adhikari S, Verma S, Sharma MR. World Health Organization Tool for Benchmarking Ethics Oversight of Health-Related Research with Human Participants. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2024;62(280):862-5. DOI: 10.31729/jnma.8839; PMCID: PMC11930055; PMID: 40654383
30. Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101. DOI: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
31. Astariyani NLG, Hermanto B, da Cruz R, Wisnaeni F. Preventive and Evaluative Mechanism Analysis on Regulatory and Legislation Reform in Indonesia. Law Reform. 2023;19(2):248–69. DOI: 10.14710/lr.v19i2.55819
32. Cipta DA, Andoko D, Theja A, Utama AVE, Hendrik H, William DG, et al. Culturally sensitive patient-centered healthcare: a focus on health behavior modification in low and middle-income nations—insights from Indonesia. Front Med. 2024;11:1353037. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1353037; PMCID: PMC11047771; PMID: 38681051
33. Hasyim H, Marini H, Misnaniarti M, Flora R, Liberty IA, Elagali A, et al. Evaluation of the malaria elimination programme in Muara Enim Regency: a qualitative study from Indonesia. Malar J. 2024;23(1):43. DOI: 10.1186/s12936-024-04857-7; PMCID: PMC10860310; PMID: 38347633
34. Julian GS, Shau WY, Chou HW, Setia S. Bridging Real-World Data Gaps: Connecting Dots Across 10 Asian Countries. JMIR Med Inform. 2024;12:e58548. DOI: 10.2196/58548; PMCID: PMC11362708; PMID: 39026427
35. Mukherjee A, Gómez-Sala B, O’Connor EM, Kenny JG, Cotter PD. Global Regulatory Frameworks for Fermented Foods: A Review. Front Nutr. 2022;9:902642. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.902642; PMCID: PMC9198641; PMID: 35719144
36. Xu L, Gao H, Kaitin KI, Shao L. Reforming China’s drug regulatory system. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018;17(12):858–9. DOI: 10.1038/nrd.2018.150; PMID: 30262888
37. Burns LR, Pauly MV. Transformation of the Health Care Industry: Curb Your Enthusiasm? Milbank Q. 2018;96(1):57-109. DOI: 10.1111/1468-0009.12312; PMCID: PMC5835686; PMID: 29504199
38. Salau AK, Shehu MS, Bakare-Odunola MT. Navigating the challenges of integrating African herbal medicines: a path to universal acceptance: herbal medicines. Fountain J Nat Appl Sci. 2024;13(1):23-36. DOI: 10.53704/fujnas.v13i1.474
39. Saggar S, Mir PA, Kumar N, Chawla A, Uppal J, Kaur A. Traditional and herbal medicines: opportunities and challenges. Pharmacogn Res. 2022;14(2):107-14. DOI: 10.5530/pres.14.2.15
40. Liang Z, Hu H, Li J, Yao D, Wang Y, Ung COL. Advancing the Regulation of Traditional and Complementary Medicine Products: A Comparison of Five Regulatory Systems on Traditional Medicines with a Long History of Use. Feng N, editor. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:5833945. DOI: 10.1155/2021/5833945; PMCID: PMC8566035; PMID: 34745290
41. Tilburt J. Herbal medicine research and global health: an ethical analysis. Bull World Health Organ. 2008;86(8):594–9. DOI: 10.2471/blt.07.042820; PMCID: PMC2649468; PMID: 18797616
42. Forssten SD, Laitila A, Maukonen J, Ouwehand AC. Probiotic triangle of success; strain production, clinical studies and product development. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2020;367(19):fnaa167. DOI: 10.1093/femsle/fnaa167; PMCID: PMC7578568; PMID: 33049046
43. Jost S, Herzig C, Birringer M. A Balancing Act—20 Years of Nutrition and Health Claims Regulation in Europe: A Historical Perspective and Reflection. Foods. 2025;14(9):1651. DOI: 10.3390/foods14091651; PMCID: PMC12071930; PMID: 40361733
44. Hojsak I, Kolaček S. Role of Probiotics in the Treatment and Prevention of Common Gastrointestinal Conditions in Children. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2024;27(1):1-14. DOI: 10.5223/pghn.2024.27.1.1; PMCID: PMC10796258; PMID: 38249642
45. Szajewska H, Vinderola G. Current Regulatory Issues for the Use of Probiotics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1449:187-93. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-58572-2_12; PMID: 39060739
46. Association of South East Asian Nations. ASEAN Guidelines on Claims and Claims Substantiation for Health Supplements. Jakarta: Association of South East Asian Nations; 2020. Available from: https://asean.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/09/ASEAN-Guidelines-on-Claims-Claims-Substantiation-HS-V2.0-with-discla....pdf
47. Ballarin L, Karahan A, Salvetti A, Rossi L, Manni L, Rinkevich B, et al. Stem Cells and Innate Immunity in Aquatic Invertebrates: Bridging Two Seemingly Disparate Disciplines for New Discoveries in Biology. Front Immunol. 2021;12:688106. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.688106; PMCID: PMC8278520; PMID: 34276677
48. Chen X, Huang J, Wu J, Hao J, Fu B, Wang Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2022;55(4):e13141. DOI: 10.1111/cpr.13141; PMCID: PMC9055891; PMID: 34936710
49. Eskens O, Amin S. Challenges and effective routes for formulating and delivery of epidermal growth factors in skin care. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2021;43(2):123–30. DOI: 10.1111/ics.12685; PMID: 33354795
50. Hebert D, Nelson J, Diehl BN, Zito P. Single-Particle ICP-MS/MS Application for Routine Screening of Nanoparticles Present in Powder-Based Facial Cosmetics. Nanomaterials. 2023;13(19):2681. DOI: 10.3390/nano13192681; PMCID: PMC10574118; PMID: 37836322
51. Pérez-Rivero C, López-Gómez JP. Unlocking the Potential of Fermentation in Cosmetics: A Review. Fermentation. 2023;9(5):463. DOI: 10.3390/fermentation9050463
52. SCCS members; Other experts. The SCCS Notes of Guidance for the testing of cosmetic ingredients and their safety evaluation, 11th revision, 30-31 March 2021, SCCS/1628/21. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2021;127:105052. DOI: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2021.105052; PMID: 34653552
53. Wijaya T. Policy Paper No. 60 Unpacking The Fintech Regulatory Sandbox Framework in Indonesia: Risks Management and The Data Privacy Imperative. Jakarta: Center for International Private Enterprise; 2023.
54. Nurrochmat DR, Pribadi R, Siregar H, Justianto A, Park MS. Transformation of Agro-Forest Management Policy under the Dynamic Circumstances of a Two-Decade Regional Autonomy in Indonesia. Forests. 2021;12(4):419. DOI: 10.3390/f12040419
55. Zhang Z, Li R, Chen Y, Yang H, Fitzgerald M, Wang Q, et al. Integration of traditional, complementary, and alternative medicine with modern biomedicine: the scientization, evidence, and challenges for integration of traditional Chinese medicine. Acupunct Herb Med. 2024;4(1):68–78. DOI: 10.1097/HM9.0000000000000089
56. Gatt AR, Vella Bonanno P, Zammit R. Ethical considerations in the regulation and use of herbal medicines in the European Union. Front Med Technol. 2024;6:1358956. DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2024.1358956; PMCID: PMC11211540; PMID: 38948354
57. Mutola S, Pemunta NV, Ngo NV. Utilization of traditional medicine and its integration into the healthcare system in Qokolweni, South Africa; prospects for enhanced universal health coverage. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2021;43:101386. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101386; PMID: 33895465
58. ASEAN Consultative Committee for Standards and Quality. Roadmap and Action Plan to Promote Smart Manufacturing Development in ASEAN. Hanoi; ASEAN Consultative Committee for Standards and Quality: 2020.
59. Karamanidou T, Bourganis V, Gatzogianni G, Tsouknidas A. A Review of the EU’s Regulatory Framework for the Production of Nano-Enhanced Cosmetics. Metals. 2021;11(3):455. DOI: 10.3390/met11030455
60. Bhat BB, Kamath PP, Chatterjee S, Bhattacherjee R, Nayak UY. Recent Updates on Nanocosmeceutical Skin Care and Anti-Aging Products. Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(15):1258–71. DOI: 10.2174/1381612828666220321142140; PMID: 35319358
61. Ferreira L, Pires PC, Fonseca M, Costa G, Giram PS, Mazzola PG, et al. Nanomaterials in Cosmetics: An Outlook for European Regulatory Requirements and a Step Forward in Sustainability. Cosmetics. 2023;10(2):53. DOI: 10.3390/cosmetics10020053
62. Ishikawa K. The ASEAN Economic Community and ASEAN economic integration. J Contemp East Asia Stud. 2021;10(1):24–41. DOI: 10.1080/24761028.2021.1891702
63. Sayuti NA, Atikah N. The pattern of herbal medicines use for breastfeeding mother in Jogonalan, Klaten, Indonesia: a mini survey. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023;23(1):399. DOI: 10.1186/s12906-023-04235-x; PMCID: PMC10629069; PMID: 37936188
64. Sari RK, Alfarizi M, Ab Talib MS. Sustainable strategic planning and management influence on sustainable performance: findings from halal culinary MSMEs in Southeast Asia. J Model Manag. 2024;19(6):2034–60. DOI: 10.1108/JM2-12-2023-0324
65. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD Regulatory Policy Outlook 2021. Paris: OECD Publishing; 2021. DOI: 10.1787/38b0fdb1-en
66. World Bank. Conditions for Effective Collaboration between Modern and Traditional Medicine. Indigenous Knowledge (IK) Notes. Washington DC: World Bank; 2004. Available from: https://hdl.handle.net/10986/10772
67. Noda S, Hernandez PMR, Sudo K, Takahashi K, Woo NE, Chen H, et al. Service Delivery Reforms for Asian Ageing Societies: A Cross-Country Study Between Japan, South Korea, China, Thailand, Indonesia, and the Philippines. Int J Integr Care. 2021;21(2):1. DOI: 10.5334/ijic.4739; PMCID: PMC8034408; PMID: 33867896
68. Hicks J. A ‘data realm’ for the Global South? Evidence from Indonesia. Third World Q. 2021;42(7):1417-35. DOI: 10.1080/01436597.2021.1901570
69. Smith EK, Kolcava D, Bernauer T. Stringent sustainability regulations for global supply chains are supported across middle-income democracies. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):1049. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45399-5; PMCID: PMC10844325; PMID: 38316803
70. Sayari S, Mgadmi N, Dhaou IB, Almehdar M, Chishty SK, Rabeh A. Advancing Sustainable Development Through Digital Transformation and Fintech Innovation. Sustainability. 2025;17(11):4924. DOI: 10.3390/su17114924
71. Tay LY, Tai HT, Tan GS. Digital financial inclusion: A gateway to sustainable development. Heliyon. 2022;8(6):e09766. DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09766; PMCID: PMC9240988; PMID: 35785228
72. Mamun AY, László V. Advancing sustainability through financial inclusion and sustainable finance: a systematic literature review. Digit Finance. 2025;7:853–70. DOI: 10.1007/s42521-025-00142-7
73. Shi W, Ba L, Zhou J, Yao J, Zhang X, Wang G, et al. Comparative Study on Pharmacovigilance Signal Management System among the European Union, the United States and Japan. Chin Pharm. 2021;12:406-12.
74. Khan MAA, Hamid S, Babar ZU. Pharmacovigilance in High-Income Countries: Current Developments and a Review of Literature. Pharmacy. 2023;11(1):10. DOI: 10.3390/pharmacy11010010; PMCID: PMC9844306; PMID: 36649020
75. Borzova MA. Real-world data: general regulatory approaches in the EU and Japan. Real-World Data Evid. 2022;2(1):11-6. DOI: 10.37489/2782-3784-myrwd-7
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohamad Kashuri, Arry Yanuar

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.