Purple Yam (Dioscorea alata) Extract Increasing Dopamine Levels and Improving the Brain's Microscopic Features in Parkinson's Model Mice
Abstract
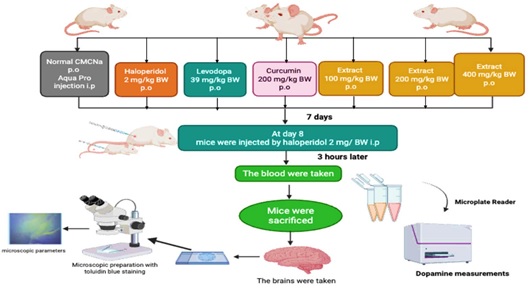
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a severe neurodegenerative disorder, that causes progressive motor issues from the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc). Purple yam (Dioscorea alata), rich in anthocyanins, shows promise as a natural antioxidant and neuroprotectant. This study investigated the antiparkinsonian effects of D. alata extract on dopamine levels and brain microscopic features in a haloperidol-induced PD mouse model. Thirty-five male mice were randomly allocated into seven groups: normal (CMC-Na and aqua pro injection), haloperidol-induced negative control (CMC-Na), positive control (levodopa 39 mg/kgBW), curcumin (200 mg/kgBW), and D. alata extract-treated groups (100, 200, and 400 mg/kgBW). Treatments were administered daily for seven days. On day 8, all groups, except the normal control, received an intraperitoneal injection of haloperidol (2 mg/kgBW) to induce Parkinsonism. Three hours post-haloperidol injection, dopamine levels were measured from orbital vein blood. Subsequently, brains were harvested for histological examination of the SNpc using Toluidine blue staining. Data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA followed by LSD post-hoc tests. The 400 mg/kgBW dose of D. alata extracts significantly increased dopamine levels (p<0.05) compared to the negative control group. Microscopic analysis of the SNpc in mice treated with 400 mg/kgBW extract revealed preserved, dark, and solid neuronal morphology, with significantly higher scoring results (p<0.05) when compared to the levodopa-treated group. These findings suggest that D. alata extract, particularly at a dose of 400 mg/kgBW, exhibits potential antiparkinsonian activity by elevating dopamine levels and mitigating dopaminergic neuronal damage in a haloperidol-induced PD mouse model.
Full text article
References
2. Kouli A, Torsney KM, Kuan WL. Parkinson’s Disease: Etiology, Neuropathology, and Pathogenesis. In: Stroker TB, Greenland JC, editors. Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications; 2018. pp 3–26. DOI: 10.15586/codonpublications.parkinsonsdisease.2018.ch1
3. Maiti P, Manna J, Dunbar GL. Current understanding of the molecular mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease: Targets for potential treatments. Transl Neurodegener. 2017;6:28. DOI: 10.1186/s40035-017-0099-z
4. DeMaagd G, Philip A. Part 2: Introduction to the Pharmacotherapy of Parkinson's Disease, With a Focus on the Use of Dopaminergic Agents. P T. 2015;40(9):590-600. PMCID: PMC4571848; PMID: 26417179
5. Dias V, Junn E, Mouradian MM. The Role of Oxidative Stress in Parkinson’s Disease. J Parkinsons Dis. 2013;3(4):461–91. DOI: 10.3233/JPD-130230; PMCID: PMC4135313; PMID: 24252804
6. Simon DK, Tanner CM, Brundin P. Parkinson's Disease Epidemiology, Pathology, Genetics, and Pathophysiology. Clin Geriatr Med. 2020;36(1):1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.cger.2019.08.002; PMCID: PMC6905381; PMID: 31733690
7. Ullah R, Khan M, Shah SA, Saeed K, Kim MO. Natural Antioxidant Anthocyanins—A Hidden Therapeutic Candidate in Metabolic Disorders with Major Focus in Neurodegeneration. Nutrients. 2019;11(6):1195. DOI: 10.3390/nu11061195; PMCID: PMC6628002; PMID: 31141884
8. Parambi DGT, Saleem U, Shah MA, Anwar F, Ahmad B, Manzar A, et al. Exploring the Therapeutic Potentials of Highly Selective Oxygenated Chalcone Based MAO-B Inhibitors in a Haloperidol-Induced Murine Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(11):2786–99. DOI: 10.1007/s11064-020-03130-y; PMID: 32939670
9. Kabra A, Baghel US, Hano C, Martins N, Khalid M, Sharma R. Neuroprotective potential of Myrica esulenta in Haloperidol induced Parkinson’s disease. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2020;11(4):448–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaim.2020.06.007; PMCID: PMC7772500; PMID: 32912644
10. Ardhianta IR, Peranginangin JM, Handayani SR. Antiparkinson Activity of Rosella Extract (Hibiscus sabbdariffa L.) in White Male (Rattus norvegicus) Sprague Dawley Rats Induced by Haloperidol. J Farmasi Indones. 2017;14(2):160–8. DOI: 10.31001/jfi.v14i2.371
11. Rai SN, Chaturvedi VK, Singh P, Singh BK, Singh MP. Mucuna pruriens in Parkinson’s and in some other diseases: recent advancement and future prospects. 3 Biotech. 2020;10(12):522. DOI: 10.1007/s13205-020-02532-7; PMCID: PMC7655893; PMID: 33194526
12. Yu D, Zhang P, Li J, Liu T, Zhang Y, Wang Q, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in Parkinson’s disease. J Pharm Anal. 2021;11(2):220–31. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.06.002; PMCID: PMC8116202; PMID: 34012698
13. Goyal A, Gopika S, Kumar A, Garabadu D. A Comprehensive Review on Preclinical Evidence-based Neuroprotective Potential of Bacopa monnieri against Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(9):889–901. DOI: 10.2174/1389450123666220316091734; PMID: 35297345
14. El Nebrisi E. Neuroprotective Activities of Curcumin in Parkinson’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(20):11248. DOI: 10.3390/ijms222011248; PMCID: PMC8537234; PMID: 34681908
15. Yuliani S, Utami D, Ramadhan MM, Raihana A, Ulfah RN, Ainiyah NP. Evaluation of antiparkinsonian activity of water yam tuber (Dioscorea alata L.) extract on haloperidol-induced Parkinson’s disease in mice. Pharmaciana. 2023;13(1):48-57. DOI: 10.12928/pharmaciana.v13i1.25590
16. Sahebnasagh A, Eghbali S, Saghafi F, Sureda A, Avan R. Neurohormetic phytochemicals in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Immun Ageing. 2022;19(1):36. DOI: 10.1186/s12979-022-00292-x
17. Srivichai S, Hongsprabhas P. Profiling Anthocyanins in Thai Purple Yams (Dioscorea alata L.). Int J Food Sci. 2020;2020(1):1594291. DOI: 10.1155/2020/1594291
18. Khoo HE, Azlan A, Tang ST, Lim SM. Anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: colored pigments as food, pharmaceutical ingredients, and the potential health benefits. Food Nutr Res. 2017;61(1):1361779. DOI: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1361779; PMCID: PMC5613902; PMID: 28970777
19. Tamaroh S, Raharjo S, Murdiati A, Anggrahini S. Perubahan Antosianin dan Aktivitas Antioksidan Tepung Uwi Ungu selama Penyimpanan. J Aplikasi Teknologi Pangan. 2018;7(1):31–6. DOI: 10.17728/jatp.2224
20. Strathearn KE, Yousef GG, Grace MH, Roy SL, Tambe MA, Ferruzzi MG, et al. Neuroprotective effects of anthocyanin- and proanthocyanidin-rich extracts in cellular models of Parkinson׳s disease. Brain Res. 2014;1555:60–77. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.01.047; PMCID: PMC4024464; PMID: 24502982
21. O’Hara DM, Kapadia M, Ping S, Kalia SK, Kalia LV. Semi-Quantitative Determination of Dopaminergic Neuron Density in the Substantia Nigra of Rodent Models using Automated Image Analysis. J Vis Exp. 2021;168:62062. DOI: 10.3791/62062; PMID: 33616088
22. Chokhawala K, Stevens L. Antipsychotic Medications. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Bookshelf ID: NBK519503; PMID: 30137788
23. Anitasari ND, Peranginangin JM, Handayani SR. Aktivitas Antiparkinson Ekstrak Rimpang Temulawak (Curcuma Xathorriza Roxb.) Pada Tikus Putih (Rattus Norvegicus) Galur Sprague Dawley Yang Diinduksi Haloperidol. J Farmasi Indones. 2017;14(2):142–53. DOI: 10.31001/jfi.v14i2.370
24. Saleem U, Chauhdary Z, Raza Z, Shah S, Rahman M, Zaib P, et al. Anti-Parkinson’s Activity of Tribulus terrestris via Modulation of AChE, α-Synuclein, TNF-α, and IL-1β. ACS Omega. 2020;5(39):25216–27. DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c03375; PMCID: PMC7542845; PMID: 33043200
25. Yuliani S, Bachri MS, Sofia V, Widyaningsih W, Muttaqien DA, Putri GR, et al. Aktivitas Ekstrak Rimpang Kunyit (Curcuma longa L) pada Mencit Parkinson yang Diinduksi Haloperidol. J Sain Veteriner. 2022;40(3):329-36. DOI: 10.22146/jsv.71871
26. Di Battista V, Hey-Hawkins E. Development of Prodrugs for Treatment of Parkinson's Disease: New Inorganic Scaffolds for Blood-Brain Barrier Permeation. J Pharm Sci. 2022;111(5):1262–79. DOI: 10.1016/j.xphs.2022.02.005; PMID: 35182542
27. Hansen CA, Miller DR, Annarumma S, Rusch CT, Ramirez-Zamora A, Khoshbouei H. Levodopa-induced dyskinesia: a historical review of Parkinson’s disease, dopamine, and modern advancements in research and treatment. J Neurol. 2022;269(6):2892–909. DOI: 10.1007/s00415-022-10963-w; PMCID: PMC9124678; PMID: 35039902
28. Pereira JB, Kumar A, Hall S, Palmqvist S, Stomrud E, Bali D, et al. DOPA decarboxylase is an emerging biomarker for Parkinsonian disorders including preclinical Lewy body disease. Nat Aging. 2023;3(10):1201–9. DOI: 10.1038/s43587-023-00478-y; PMCID: PMC10570139; PMID: 37723208
29. DeMaagd G, Philip, A. Parkinson’s Disease and Its Management: Part 1: Disease Entity, Risk Factors, Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Diagnosis. P T. 2015;40(8):504–32. PMCID: PMC4517533; PMID: 26236139
30. Baweja GS, Gupta S, Kumar B, Patel P, Asati V. Recent updates on structural insights of MAO-B inhibitors: a review on target-based approach. Mol Divers. 2024;28(3):1823-45. DOI: 10.1007/s11030-023-10634-6; PMCID: PMC10047469; PMID: 36977955
31. Pratiwi IN, Aligita W, Kaniawati M. A study of antioxidant potential from herbal plants and the effects on Parkinson’s disease. J Ilmiah Farmasi. 2021;17(1):80–95. DOI: 10.20885/jif.vol17.iss1.art9
32. El-Shamarka MES, Abdel-Salam OM, Shafee N, Zeidan HM. Curcumin modulation of L-dopa and rasagiline-induced neuroprotection in rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2023;26(2):139–47. DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2022.61687.13650; PMCID: PMC9869885; PMID: 36742141
33. Priska M, Peni N, Carvallo L, Ngapa YD. Review: Antosianin dan Pemanfaatannya. Cakra Kimia Indones J Appl Chem. 2019;6(2):79–97. DOI: 10.24843/CK.2018.v06.i02.46629
Authors
Copyright (c) 2025 Sapto Yuliani, Dwi Utami, Laela Hayu Nurani, Muhammad Marwan Ramadhan, Nadia Putri Ainiyah, Mochammad Saiful Bachri, Wahyu Widyaningsih, Danang Prasetyaning Amukti

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.