Evaluation of Rational Drug Use based on Indicators of Diseases and Facilities at Community Health Centers in Districts in Semarang
Abstract
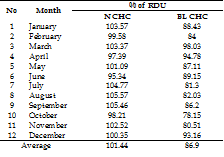
Rational drug use (RDU) is an indicator to evaluates a treatment given to patients, like proper medication, precise diagnosis, precise dosing. Community Health Center (CHC) has the risk of irrational drug use. In this study, researchers selected N and BL CHC, aiming to evaluate the prescribing indicators based on three diseases which are non-pneumonia acute respiratory infection (ARI), non-specific diarrhea and myalgia, and the facility indicators with DOEN (list of essential national medicines) availability and 20 mandatory drugs. This research was a descriptive-analytical study with cross-sectional methods where the data retrieval of the prescribing is taken from January to December 2018. The study used the normality test and homogeneity test before independent sample T-test, from the third outcome of the test, the N and BL CHC could be said to differ significantly of RDU. It can be concluded that rational drug use is reviewed from a prescribing indicator based on disease and facility indicator. The results of RDU are rational in N CHC, in contrast with BL CHC which is not rational with the results of the RDU in N CHC is 101.44% and BL CHC is 89.81%. The results of N CHC is better than BL CHC, which both CHCs have fulfilled the target of the government, for 68% in 2018. In both CHCs for the facility indicator, there are a DOEN and 20 essential medicines.
Full text article
References
Crawford, S.E., Ramani, S., Tate, J.E., Parashar, U.D., Svensson, L., Hagbom, M., Franco, M.A., Grenberg, H.B., O’Ryan, M., Kang, G., Desselberger, U., Estes, M.K. 2017. Rotavirus infection. Nature Reviews Disease Primers. 3:17083. https://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.83
Dahlan, M.S. 2014. Statistik Untuk Kedoteran dan Kesehatan Edisi 6. Jakarta: Epidemiologi Indonesia.
FitzGerald, R.J. 2009. Medication errors: the importance of an accurate drug history. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 67(6):671-675. https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03424.x
Kardela. W., Retnosari, A., Sudibyo, S. 2014. Perbandingan Penggunaan Obat Rasional Berdasarkan Indikator WHO di Puskesmas Kecamatan antara Kota Depok dan Jakarta Selatan. Jurnal Kefarmasian Indonesia. 4(2):91-102.
Kukreja, S., Kalra, G., Shah, N., Shrivastava, A. 2013. Polypharmacy in Psychiatry: A Review. Mens Sana Monographs. 11(1):82-99. https://dx.doi.org/10.4103/0973-1229.104497
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. 2011. Modul Penggunaan Obat Rasional. Jakarta: Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. 2013. Daftar Obat Esensial Nasional 2013. Jakarta: Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. 2017. Laporan Akuntabilitas Kinerja 2016. Jakarta: Directorate General of Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia
Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia. 2018. Laporan Kinerja Direktorat Jenderal Kefarmasian dan Alat Kesehatan Tahun 2017. Jakarta: Directorate General of Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Ministry of Health of the Republic of Indonesia.
Ofori-Asenso, R., Agyeman, A.A. 2016. Irrational Use of Medicines—A Summary of Key Concepts. Pharmacy. 4(4):35. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pharmacy4040035
Sauriasari, R., Aulia, A.A.H., Swastika, A. 2017. Evaluasi kesesuaian penulisan resep pada kasus ISPA non-pneumonia di poli MTBS Puskesmas Kecamatan Cengkareng Jakarta. Pharmaceutical Sciences & Research. 4(2):81-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.7454/psr.v4i2.3770
Semarang City Health Office. 2015. Profil Kesehatan Kota Semarang Tahun 2014. Semarang: Semarang City Health Office
Simatupang, A. 2012. Pedoman WHO Tentang Penulisan Resep yang Baik sebagai Penggunaan Obat yang Rasional. Jakarta: Faculty of Medicine, Indonesian Christian University.
Smeulers, M., Verweij, L., Maaskant, J.M., de Boer, M., Krediet, C.T.P., van Dijkum, E.J.M.N., Vermeulen, H. 2015. Quality Indicators for Safe Medication Preparation and Administration: A Systematic Review. PLoS One. 10(4):e0122695. https://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122695
Authors
Copyright (c) 2019 Nisa Febrinasari, Abdur Rosyid, Leny Angelina

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.