Active Fractions of Methanol Crude Obtained from Acacia seyal gum: Antioxidant Capacity using FTIR Analysis
Abstract
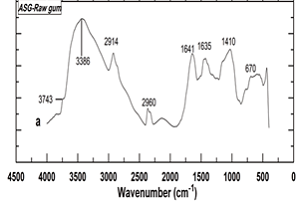
The present study is on Acacia seyal gum (ASG), which is an exudate from Talha tree. It provides a rich source of polyphenolics compounds that are used traditionally in folk medicine. The study aims to determine the antioxidant capacity (AC) and functional groups of ASG and Prebio-T-commercial (PTC) samples. The methanol crude extracts of both ASG and PTC have fractioned into chloroform (CHF), hexane (HF), acetone (AF) and methanol (MF) using solvent-solvent portion. Both ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC) assays for each fraction examined. Crude methanol extracts (CME) and its active compositions also analysed carefully using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) technique. The findings presented a wide variety of functional groups provided by the FTIR spectra (eights bands approximately. Regarding cupric reducing antioxidant capacity (CUPRAC), the methanol crude extracts values are 888.6±4.57 mg TE/100g extract, for PTC as compared to 474.3± 2.23 mg TE/100g of extract for ASG. However, both methanol and acetone fractions revealed significantly (p ≤ 0.05) high FRAP values ranged between 599.8±7.5 and 741.8±5.8 mg TE/100g fraction; for PTC and ASG, respectively. While CUPRAC showed insignificant (p ≥ 0.05) same values 356.1±2.62 mg TE/100g of fraction; for MF of both PTC and ASG respectively. Therefore, in this study, methanolic fractions (MFs) are found to be more effective than acetone fractions (AFs), except for CHF and HF. Finally, the antioxidant activity of the active fraction has provided some evidence regarding its functional groups which may have used in traditional medicine.
Full text article
References
Ali, B.H., Al-Husseni, I., Beegam, S., Al-Shukaili, A., Nemmar, A., Schierling, S., Queisser, N., Schupp, N. 2013a. Effect of gum arabic on oxidative stress and inflammation in adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. PLoS One. 8(2):e55242. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055242
Ali, B.H., Beegam, S., Al-Lawati, I., Waly, M.I., Al-Za’abi, M., Nemmar, A. 2013b. Comparative efficacy of three brands of gum acacia on adenine-induced chronic renal failure in rats. Physiological Research. 62(1):47-56.
Anderson, D.M.W. 1993. Some factors influencing the demand for gum arabic (Acacia senegal (L.) Wild.) _and other water-soluble tree exudates. Forest Ecology and Management. 58(1-2):1-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1127(93)90127-9
Apak, R., Güçlü, K., Özyürek, M., Çelik, S.E. 2008. Mechanism of antioxidant capacity assays and the CUPRAC (cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity) assay. Microchimica Acta. 160(4):413-419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-007-0777-0
Barth, A., Zscherp, C. 2002. What vibrations tell about proteins. Quarterly Reviews of Biophysics. 35(4):369-430. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033583502003815
Boulet, J.C., Williams, P., Doco, T. 2007. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy study of wine polysaccharides. Carbohydrate Polymers. 69(1):79-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.09.003
Chawla, R., Patil, G.R. 2010. Soluble Dietary Fiber. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety. 9(2):178-196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1541-4337.2009.00099.x
Doi, Y., Ichihara, T., Hagiwara, A., Imai N., Tamano, S., Orikoshi, H., Ogasawara, K., Sasaki, Y., Nakamura, M., Shirai, T. 2006. A ninety-day oral toxicity study of a new type of processed gum arabic, from Acacia tree (Acacia senegal) exudates, in F344 rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 44(4):560-566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2005.09.002
Elnour, A.A.M. 2007. Fractionation; Physicochemical and Functional properties of Acacia Polyacantha gum. Thesis. University of Khartoum, Sudan.
Elnour, A.A.M., Mirghani, M.E.S., Kabbashi, N.A., Alam, M.Z., Musa, K.H. 2018. Study of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Crude Methanol Extract and Fractions of Acacia seyal Gum. American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics. 5(1):3. https://doi.org/10.21767/2393-8862.100012
Glover, D.A., Ushida, K., Phillips, A.O., Riley, S.G. 2009. Acacia(sen) SUPERGUM™ (Gum arabic): An evaluation of potential health benefits in human subjects. Food Hydrocolloids. 23(8):2410-2415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2009.06.020
Godic, A., Poljšak, B., Adamic, M., Dahmane, R. 2014. The Role of Antioxidants in Skin Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longetivity. 2014:860479. https://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/860479
Jayasri, D., Narayanan, S.S. 2007. Manganese(II) hexacyanoferrate based renewable amperometric sensor for the determination of butylated hydroxyanisole in food products. Food Chemistry. 101(2):607-614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.02.021
Kaewseejan, N., Sutthikhum, V., Siriamornpun, S. 2015. Potential of Gynura procumbens leaves as source of flavonoid-enriched fractions with enhanced antioxidant capacity. Journal of Functional Foods. 12:120-128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2014.11.001
Kannan, R.R.R., Arumugam, R., Anantharaman, P. 2011. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis of Seagrass Polyphenols. Current Bioactive Compounds. 7(2):118-125. https://doi.org/10.2174/157340711796011142
Kupchan, S.M., Steyn, P.S., Grove, M.D., Horsfield, S.M., Meitner, S.W. 1969. Tumor inhibitors. XXXV. Myrsine saponin, the active principle of Myrsine africana L. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 12(1):167-169. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00301a045
Lebon, M., Zazzo, A., Reiche, I. 2014. Screening in situ bone and teeth preservation by ATR-FTIR mapping. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 416:110-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.08.001
Lopez-Torrez, L., Nigen, M., Williams, P., Doco, T., Sanchez, C. 2015. Acacia senegal vs. Acacia seyal gums – Part 1: Composition and structure of hyperbranched plant exudates. Food Hydrocolloids. 51:41-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.04.019
Magid, T.D.A., Eltayb, M.T.A., Dirar, A.M.A. 2014. Equalizing Gum Codal Term (a Code E414), of Acacia Senega1 (L) with Acacia Seyal (Del.), and its Impact on Gum Production and Exportation. Journal of Applied and Industrial Sciences. 2(3):144-151.
Manrique, G.D., Lajolo, F.M. 2002. FT-IR spectroscopy as a tool for measuring degree of methyl esterification in pectins isolated from ripening papaya fruit. Postharvest Biology and Technology. 25(1):99-107. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-5214(01)00160-0
Minzanova, S.T., Mironov, V.F., Arhipova, D.M., Khabibullina, A.V., Mironova, L.G., Zakirova, Y.M., Milyukov, V.A. 2018. Biological Activity and Pharmacological Application of Pectic Polysaccharides: A Review. Polymers. 10(12):1407. https://dx.doi.org/10.3390/polym10121407
Musa, H.H., Ahmed, A.A., Musa, T.H., Fedail, J.S. 2015. Gum arabic down-regulate PPAR-γ and SCD mRNA expression in mice. Polish Annals of Medicine. 22(1):11-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.poamed.2015.03.008
Musa, K.H., Abdullah, A., Kuswandi B., Hidayat, M.A. 2013. A novel high throughput method based on the DPPH dry reagent array for determination of antioxidant activity. Food Chemistry. 141(4):4102-4106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.06.112
Niu, F., Niu, D., Zhang, H., Chang, C., Gu, L., Su, Y., Yang, Y. 2016. Ovalbumin/gum arabic-stabilized emulsion: Rheology, emulsion characteristics, and Raman spectroscopic study. Food Hydrocolloids. 52:607-614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.08.010
Ouhaddouch, H., Cheikh, A., Idrissi, M.O.B., Draoui, M., Boutia, M. 2019. FT-IR Spectroscopy Applied for Identification of a Mineral Drug Substance in Drug Products: Application to Bentonite. Journal of Spectroscopy. 2019:2960845. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2960845
Sanchez, C., Nigen, M., Tamayo, V.M., Doco, T., Williams, P., Amine, C., Renard, D. 2018. Acacia gum: History of the future. Food Hydrocolloids. 78:140-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.04.008
Rehman, K.U., Wingertzahn, M.A., Teichberg, S., Harper, R.G., Wapnir, R.A. 2003. Gum arabic (GA) modifies paracellular water and electrolyte transport in the small intestine. Digestive Diseases and Sciences. 48(4):755-760. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1022845011192
Reinholds, I., Bartkevics, V., Silvis, I.C.J., van Ruth, S.M., Esslinger, S. 2015. Analytical techniques combined with chemometrics for authentication and determination of contaminants in condiments: A review. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 44:56-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2015.05.004
Renard, D., Lavenant-Gourgeon, L., Ralet, M.C., Sanchez, C. 2006. Acacia senegal gum: continuum of molecular species differing by their protein to sugar ratio, molecular weight, and charges. Biomacromolecules. 7(9):2637-2649. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060145j
Synytsya, A., Čopıkováa, J., Matějkab, P., Machovič, V. 2003. Fourier transform Raman and infrared spectroscopy of pectins. Carbohydrate Polymers. 54(1):97-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-8617(03)00158-9
Tagne, R.S., Telefo, B.P., Nyemb, J.N., Yemele, D.M., Njina, S.N., Goka, S.M., Lienou, L.L., Nwabo-Kamdje, A.H., Moundipa, P.F., Farooq, A.D. 2014. Anticancer and antioxidant activities of methanol extracts and fractions of some Cameroonian medicinal plants. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine. 7S1:S442-S447. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60272-8
Tiss, A., Carrière, F., Verger, R. 2001. Effects of Gum Arabic on Lipase Interfacial Binding and Activity. Analytical Biochemistry. 294(1):36-43. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2001.5095
Vinod, V.T.P., Sashidar, R.B., Sarma, V.U.M., Raju, S.S. 2010. Comparative amino acid and fatty acid compositions of edible gums kondagogu (Cochlospermum gossypium) and karaya (Sterculia urens). Food Chemistry. 123(1):57-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.127
Wang, H., Williams, P.A., Senan, C. 2014. Synthesis, characterization and emulsification properties of dodecenyl succinic anhydride derivatives of gum Arabic. Food Hydrocolloids. 37:143-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2013.10.033
Authors
Copyright (c) 2019 Ahmed Adam M Elnour, Mohamed Elwathig Saeed Mirghani, Nassereldeen A Kabbashi, Md Zahangir Alam, Khalid Hamid Musa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.