Level of Cytokine Interleukin-6 and Interleukin 1-β on Infectious Rat Model Treated with Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M. Smith Fruit Extract as Immunomodulator
Abstract
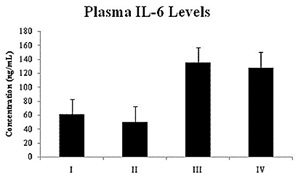
Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M Smith or locally in Southeast Sulawesi known as Wualae fruit has activity as an immunomodulator by increasing phagocytosis activity. Prior studies have been conducted to observe the effect of E. elatior as an immunomodulator, thus further study is needed to observe the production of cytokines such as IL-1β and IL-6 which are responsible for the immune responses. Etlingera elatior fruit macerated with 96% ethanol for three days and produced a total of ±74.6 g concentrated extract. Experimental animals used were divided into four groups (n=4) and treated orally once a day for seven days as follows: group I (0.5% Na CMC); group II (Stimuno®); group III (E. elatior fruit extract dose of 300 mg/kg BW); and group IV (E. elatior fruit extract dose of 400 mg/kg BW). On the eight-day, animals were infected with Staphylococcus aureus intraperitoneally and left for an hour. Thereafter, blood was collected and assayed using ELISA Kit (Elabscience rat IL-1β and Elabscience rat IL-6). Results demonstrated that group IV increased levels of IL-1β and group III and IV increased level of IL-6 (p<0.05). Increased levels of IL-1β and IL-6 are associated with phagocytosis in the immune response. In conclusion, E. elatior fruit extract at doses of 300 and 400 mg/kg BW increases levels of IL-1β and IL-6.
Full text article
References
Atri, C., Guerfali, F.Z., & Laouini, D. (2018). Role of Human Macrophage Polarization in Inflammation during Infectious Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1801. doi:10.3390/ijms19061801
Bascones-Martinez, A., Mattila, R., Gomez-Font, R., & Meurman, J.H. (2014). Immunomodulatory drugs: Oral and systemic adverse effects. Medicina Oral Patologia Oral y Cirugia Bucal, 19(1), 24-31. doi:10.4317/medoral.19087
Besung, I. N. K., Astawa, N. M., Suata, K., & Suwiti, K. (2016). Hubungan Antara Aktivasi Makrofag Dengan Kadar Interleukin-6 Dan Antibodi Terhadap Salmonella Typhi Pada Mencit (Relationship between the Macrophage Activity with Interleukin-6 Levels and Titers of Antibodies against Salmonella typhi). Jurnal Kedokteran Hewan, 10(1), 1–4. doi:10.21157/j.ked.hewan.v10i1.3359
Catanzaro, M., Corsini, E., Rosini, M., Racchi, M., & Lanni, C. (2018). Immunomodulators Inspired by Nature: A Review on Curcumin and Echinacea. Molecules, 23(11), 2778. doi:10.3390/molecules23112778
Chaplin, D.D. (2010). Overview of the Immune Response. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 125(2 Suppl 2), 3-23. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2009.12.980
Duque, G.A., & Descoteaux, A. (2014). Macrophage cytokines: Involvement in immunity and infectious diseases. Frontiers in Immunology, 5, 491. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2014.00491
Farida, S. & Maruzy, A. (2016). Kecombrang (Etlingera elatior): Sebuah Tinjauan Penggunaan Secara Tradisional, Fitokimia Dan Aktivitas Farmakologinya. Jurnal Tumbuhan Obat Indonesia, 9(1), 19-28. doi:10.22435/toi.v9i1.6389.19-28
Fristiohady, A., Zubaydah, W.O.S., Wahyuni, W., Mirda, M., Saripuddin, S., Andriani, R., Purnama, L.O.M.J., & Sahidin, S. (2019). Immunomodulator Activity of Effervescent Granule of Wualae Fruit (Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M. Smith) Based on Specific Phagocytic Activity. Borneo Journal of Pharmacy, 2(2), 35–40. doi:10.33084/bjop.v2i2.868
Ginwala, R., Bhavsar, R., Chigbu, D.G.I., Jain, P., & Khan, Z.K. (2019). Potential Role of Flavonoids in Treating Chronic Inflammatory Diseases with a Special Focus on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Apigenin. Antioxidants, 8(2), 35. doi:10.3390/antiox8020035
Handayani, V., Ahmad, A.R., & Sudir, M. (2014). Uji Aktivitas Antioksidan Ekstrak Metanol Bunga dan Daun Patikala (Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M.Sm) Menggunakan Metode DPPH. Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 1(2), 86–93. doi:10.7454/psr.v1i2.3321
Hariyanti, Sunaryo, H., & Nurlaily, S. (2015). Efek Imunomodulator Fraksi Etanol Dari Ekstrak Etanol 70% Kulit Buah Manggis (Garcinia mangostana L.) Berdasarkan Peningkatan Aktivitas Dan Kapasitas Fagositosis Sel Makrofag Peritoneum Mencit Secara In Vitro. PHARMACY: Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia (Pharmaceutical Journal of Indonesia), 12(1), 58-69.
Juwita, T., Puspitasari, I.M., & Levita, J. (2018). Torch Ginger (Etlingera elatior): A Review on its Botanical Aspects, Phytoconstituents and Pharmacological Activities. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 21(4), 151-165. doi:10.3923/pjbs.2018.151.165
Kany, S., Vollrath, J.T., & Relja, B. (2019). Cytokines in Inflammatory Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 6008. doi:10.3390/ijms20236008
Lachumy, S.J.T., Sasidharan, S., Sumathy, V., & Zakaria, Z. (2010). Pharmacological activity, phytochemical analysis and toxicity of methanol extract of Etlingera elatior (torch ginger) flowers. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine, 3(10), 769-774. doi:10.1016/S1995-7645(10)60185-X
Lopez-Castejon, G. & Brough, D. (2011). Understanding the mechanism of IL-1β secretion. Cytokine and Growth Factor Reviews, 22(4), 189–195. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.10.001
Panche, A.N., Diwan, A.D., & Chandra, S.R. (2016). Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of Nutritional Science, 5, 47. doi:10.1017/jns.2016.41
Sahidin, Salsabila, S., Wahyuni, Fristiohady, A., & Imran. (2019). Potensi Antibakteri Ekstrak Metanol dan Senyawa Aromatik dari Buah Wualae (Etlingera elatior). Jurnal Kimia Valensi, 5(1), 1-7. doi:10.15408/jkv.v5i1.8658
Sahoo, M., Ceballos-Olvera, I., Del Barrio, L., & Re, F. (2011). Role of the inflammasome, IL-1β, and IL-18 in bacterial infections. The Scientific World Journal, 11, 2037–2050. doi:10.1100/2011/212680
Syarif, R.A., Sari, F., & Ahmad, A.R. (2015). Torch ginger (Etlingera elatior Jack.) rhizomes as phenolic sources. Jurnal Fitofarmaka Indonesia, 2(2), 102–106. doi:10.33096/jffi.v2i2.178
Wahyuni, Malaka, M.H., Fristiohady, A., Yusuf, M.I., & Sahidin. (2017). Potensi Imunomodulator Ekstrak Etanol Buah Kecombrang (Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M. Smith) Terhadap Aktivitas Fagositosis Makrofag Mencit Jantan Galur Balb/C. Pharmacon, 6(3), 350–355.
Authors
Copyright (c) 2020 Adryan Fristiohady, Wahyuni Wahyuni, Fadhliyah Malik, Muhammad Ilyas Yusuf, Wa Ode Salma, Rini Hamsidi, Fredy Talebong, Yuliansyah Yuliansyah, La Ode Muhammad Julian Purnama, Saripuddin Saripuddin, Sahidin Sahidin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors continue to retain the copyright to the article if the article is published in the Borneo Journal of Pharmacy. They will also retain the publishing rights to the article without any restrictions.
Authors who publish in this journal agree to the following terms:
- Any article on the copyright is retained by the author(s).
- The author grants the journal the right of first publication with the work simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share work with an acknowledgment of the work authors and initial publications in this journal.
- Authors can enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of published articles (e.g., post-institutional repository) or publish them in a book, with acknowledgment of their initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their websites) prior to and during the submission process. This can lead to productive exchanges and earlier and greater citations of published work.
- The article and any associated published material are distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.